628
442700/A
What is sampling?
The information from the transducer on the CS90 system is a continuous flow of analogue
data. In signal processing,
sampling
is the reduction of this continuous signal to a discrete
signal.
A common example is exactly what we do in the CS90 system. We convert a sound
wave (which is an analogue
continuous-time signal
) to a sequence of samples (which is a
discrete-time signal
). A discrete (or discrete-time) signal is a sequence of data capsules. This
typically a signal that has been sampled from a continuous-time signal. Unlike a continuous
signal, a discrete signal is not a function of a time argument, but a sequence of quantities, a
function over a domain of discrete integers. Each value in the sequence is called a
sample
.
Using this technique, the analogue signal is converted to a stream of discrete signals.
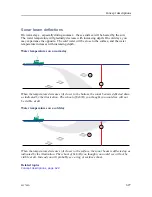
In this coordinate system,
the Y-axis is voltage (or
“volume”) and the X-axis
is time.
A
This is a continuous
flow of data, an
analogue signal, for
example an echo.
B
This line identifies the
samples that the system is extracting from the analogue signal. Each sample is identified
with the time it was taken. It will contain the value of the analogue signal at that time.
C
The distance between each vertical line is the time between each sample. This time is
identified as the sampling rate.
Related topics
Concept descriptions, page 622
Simrad CS90 Reference Manual
Summary of Contents for Simrad CS90
Page 1: ...kongsberg com simrad Simrad CS90 REFERENCE MANUAL ...
Page 2: ......
Page 627: ...442700 A 625 Related topics Concept descriptions page 622 Concept descriptions ...
Page 683: ......
Page 684: ... 2021 Kongsberg Maritime ISBN 978 82 8066 213 2 ...
Page 685: ......
Page 686: ...Reference Manual Simrad CS90 ...