Section 2: General operation
Model DMM7510 7½ Digit Graphical Sampling Multimeter Reference Manual
2-104
DMM7510-901-01 Rev. B / May 2015
Settings available for AC current measurements
See
(on page 2-26) for settings that are available when you are making
AC current measurements.
Resistance measurements
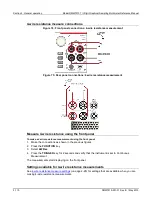
You can make 2-wire or 4-wire resistance measurements with the Model DMM7510.
For resistances more than 1 k
Ω
, the two-wire method is typically used for measurements. For
resistances less than 1 k
Ω
, use the 4-wire measurement method to cancel the effect of test-lead
resistance.
Do not apply more than 1000 V
peak
between INPUT HI and LO. Failure to observe this caution may
result in instrument damage.
For high resistance measurements in a high humidity environment, use Teflon
TM
insulated cables to
minimize errors due to cable leakage.
Two-wire compared to four-wire measurements
You can use 2-wire or 4-wire measurement techniques with the Model DMM7510.
You should use 4-wire, or remote sense, measurement techniques for the following conditions:
•
Low impedance applications
•
When measuring impedance that is less than 100 K
Ω
Use 4-wire connections when you are concerned about voltage drops because of lead or contact
resistance that could affect measurement accuracy. This can occur on low impedance devices when
you are measuring through a relay switch card and the channel on resistance.
You can use the 2-wire, or local sense, measurement technique for the following measure conditions
when the voltage drop due to the 2-wire test current and cable lead resistance is minimal compared
to the resistance of the device under test.