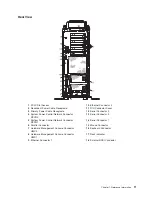
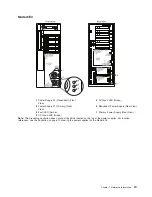
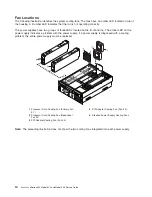
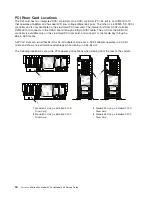
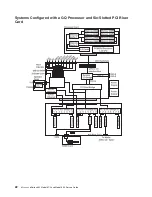
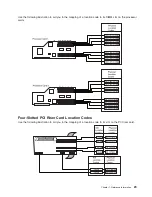
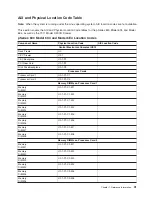
AIX Location Codes
Note:
When the system is running under the Linux operating system, AIX location codes are not available.
The basic formats of the AIX location codes are as follows:
v
For non-SCSI devices/drives:
– AB-CD-EF-GH
v
For SCSI devices/drives:
– AB-CD-EF-G,H
Non-SCSI Devices/Drives
For planars, cards, and non-SCSI devices, the location code is defined as follows:
AB-CD-EF-GH
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Device/FRU/Port ID
|
|
Connector ID
|
devfunc Number, Adapter Number or Physical Location
Bus Type or PCI Parent Bus
v
The AB value identifies a bus type or PCI parent bus as assigned by the firmware.
v
The CD value identifies adapter number, the adapter’s devfunc number, or physical location. The
devfunc number is defined as the PCI device number times 8, plus the function number.
v
The EF value identifies a connector.
v
The GH value identifies a port, address, device, or FRU.
Adapters and cards are identified only with AB-CD.
The possible values for AB are:
00
Processor bus
01
ISA bus
02
EISA bus
03
MCA bus
04
PCI bus used in the case where the PCI bus cannot be identified
05
PCMCIA buses
xy
For PCI adapters where x is equal to or greater than 1. The x and y are characters in the range of 0-9, A-H,
J-N, P-Z (O, I, and lowercase are omitted) and are equal to the parent bus’s ’ibm, aix-location’ open firmware
property.
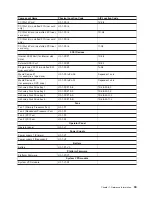
The possible values for CD depend on the adapter/card:
v
For pluggable PCI adapters/cards, CD is the device’s devfunc number (PCI device number times 8, plus
the function number). The C and D are characters in the range of 0-9, and A-F (hex numbers). Location
codes therefore uniquely identify multiple adapters on individual PCI cards.
v
For pluggable ISA adapters, CD is equal to the order of the ISA cards defined/configured either by SMIT
or the ISA Adapter Configuration Service Aid.
v
For integrated ISA adapters, CD is equal to a unique code identifying the ISA adapter. In most cases,
this code is equal to the adapter’s physical location code. In cases where a physical location code is not
available, CD will be FF.
EF is the connector ID. It is used to identify the adapter’s connector to which a resource is attached.
GH is used to identify a port, device, or FRU. For example:
v
For ASYNC devices, GH defines the port on the fanout box. The values are 00 to 15.
v
For a diskette drive, H identifies either diskette drive 1 or 2. G is always 0.
v
For all other devices, GH is equal to 00.
24
Eserver
pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide
Summary of Contents for @Server pSeries 630 6C4
Page 1: ...pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide SA38 0604 03 ERserver...
Page 2: ......
Page 3: ...pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide SA38 0604 03 ERserver...
Page 16: ...xiv Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 18: ...xvi Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 382: ...362 Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 440: ...420 Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 538: ...System Parts continued 518 Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 541: ...Chapter 10 Parts Information 521...
Page 562: ...542 Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 568: ...548 Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 576: ...556 Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 580: ...560 Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 616: ...596 Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 646: ...626 Eserver pSeries 630 Model 6C4 and Model 6E4 Service Guide...
Page 649: ......