189
Configuring DNS
Overview
Domain Name System (DNS) is a distributed database that provides TCP/IP applications with the
mappings between host names and IP addresses. With DNS, you can use easy-to-remember host names
in some applications and let the DNS server translate them into correct IP addresses.
For more information about DNS, see
Layer 3—IP Services Configuration Guide
in
HP MSR Router Series
Configuration Guides (V5)
.
DNS provides the following functions:
•
Dynamic domain name resolution
—Implemented by querying the DNS server.
•
DNS proxy
—Forwards DNS requests and replies between the DNS client and DNS server.
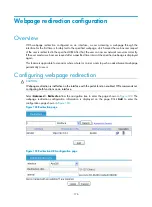
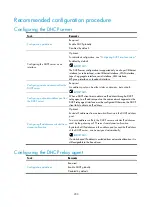
Recommended configuration procedure
Configuring dynamic domain name resolution
Task Remarks
Enabling dynamic domain name resolution
Required.
Enable dynamic domain name resolution.
Disabled by default.
Required.
Not specified by default.
You can specify up to six DNS servers.
Configuring a domain name suffix
Optional.
A suffix is used when the name to be resolved is incomplete. The
system can supply the missing part. For example, a user can
configure com as the suffix for aabbcc.com. The user only needs
to enter aabbcc to obtain the IP address of aabbcc.com because
the system adds the suffix and delimiter before passing the name
to the DNS server.
Not configured by default.
You can configure up to ten DNS suffixes.
Clearing the dynamic domain name cache
Optional.
Clear the dynamic IPv4 domain name cache.
The DNS client stores latest mappings between domain names
and IP addresses in the dynamic domain name cache. The DNS
client searches the cache for a repeated query rather than sends
a request to the DNS server. The mappings are aged out from the
cache after a certain time. You can also manually clear the
cache.
Summary of Contents for MSR SERIES
Page 17: ...xv Documents 835 Websites 835 Conventions 836 Index 838 ...
Page 20: ...3 Figure 3 Initial page of the Web interface ...
Page 42: ...25 Figure 13 Firefox Web browser setting ...
Page 59: ...42 Figure 27 Checking the basic service configuration ...
Page 73: ...56 Figure 35 Sample interface statistics ...
Page 156: ...139 Figure 139 Rebooting the 3G modem ...
Page 168: ...151 Figure 152 Configuring Web server 2 ...
Page 174: ...157 Figure 158 Configure the URL filtering function ...
Page 242: ...225 Figure 233 Enabling the DHCP client on interface Ethernet 0 1 ...
Page 247: ...230 Figure 236 The page for configuring an advanced IPv4 ACL ...
Page 255: ...238 Figure 241 Advanced limit setting ...
Page 298: ...281 e Click Apply 2 Configure Router B in the same way Router A is configured ...
Page 400: ...383 Figure 387 Verifying the configuration ...
Page 405: ...388 ...
Page 523: ...506 Figure 530 Ping configuration page ...
Page 775: ...758 Figure 785 Configuring a jump node ...