Dimensions and Standards
Standards
Functional:
ISO 8802/3, IEEE 802.3, 802.3u
Safety:
UL 60950-1, EN 60950-1, CSA 22.2 #60950-1,
IEC60950-1
EMC:
EN 55022 Class B, EN 55024,
FCC Part 15 Class B*
ICES-003 Class B
Environmental: EN 60068 (IEC 68)
Category 5 screened cables must be used to ensure compliance
with the Class B requirements of the above standards. The use of
unscreened cables complies with the Class A requirements.
* Refer to Regulatory Notices in the Support and Safety Information sheet.
Operating Conditions
HP V1405-5G Switch
3.4W / 12BTU/hr
HP V1405-8G Switch
4W / 14BTU/hr
HP V1405-5 Switch
3.8W / 13BTU/hr
HP V1405-8 Switch
4.7W / 16.5BTU/hr
0 to 40ºC (32 to 104ºF)
operating temperature
0 to 95% (non-
condensing) humidity
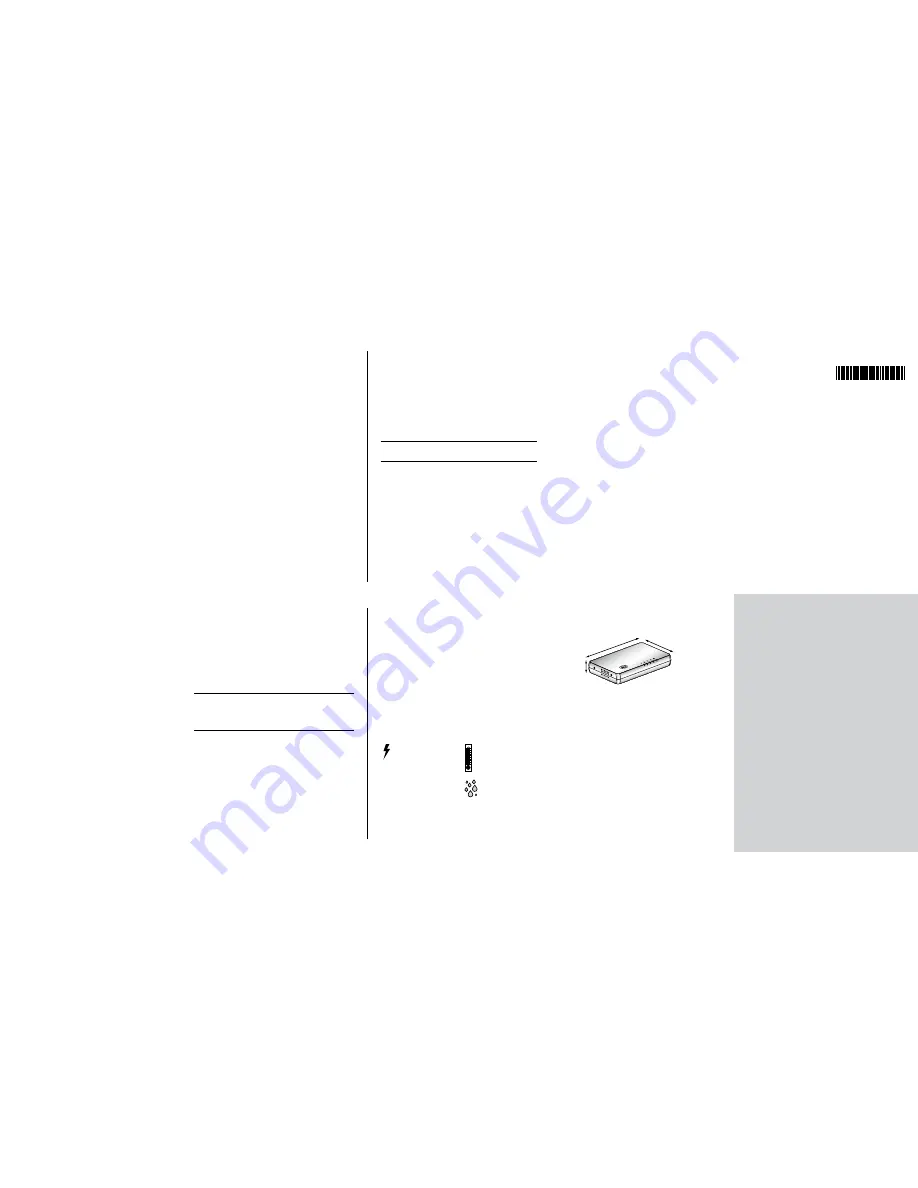
Dimensions
HP V1405-5G Switch
1
Height: 30 mm (1.18 in.)
2
Width: 178 mm (7.00 in.)
3
Depth: 108 mm (4.25 in.)
Weight: 275g (9.7 ounces)
HP V1405-5 Switch
1
Height: 30 mm (1.18 in.)
2
Width: 143 mm (5.60 in.)
3
Depth: 108 mm (4.25 in.)
Weight: 255g (8.99 ounces)
HP V1405-8G Switch
1
Height: 30 mm (1.18 in.)
2
Width: 178 mm (7.00 in.)
3
Depth: 108 mm (4.25 in.)
Weight: 310g (10.93 ounces)
HP V1405-8 Switch
1
Height: 30 mm (1.18 in.)
2
Width: 143 mm (5.60 in.)
3
Depth: 108 mm (4.25 in.)
Weight: 308g (10.87 ounces)
HP V1405-5 Switch (JD866A)
HP V1405-8 Switch (JD867A)
HP V1405-5G Switch (JD869A)
HP V1405-8G Switch (JD871A)
Installation Guide
Connecting Workstations
Twisted Pair (TP) Cables
Cables can be shielded (screened) or unshielded. Cables must be
Category 5 or above. HP recommends Category 5E or 6 cable for
Gigabit connections. The maximum length you can use is 100 m
(328 ft).
Twisted Pair (TP) cable is very easy to use. To connect a TP cable,
simply slot the connector into the relevant RJ-45 Port. When a
connector is fully in, its latch locks into place. To disconnect the
cable, push the connector’s latch in and remove it.
When one end of a TP cable is connected to the Switch and
the other end is connected to the network interface card of a
workstation or other device, the Switch will automatically detect
whether a straight-through or crossover cable is being used and
will compensate if required. The units will then autonegotiate to
determine the fastest possible link speed between them. This may
take a few seconds and the outcome will be reflected in the LEDs
on the front of the Switch.
If the equipment connected to the Switch does not support
autonegotiation or it has been disabled, it must be configured to
operate in half duplex mode.
Problem Solving
The Switch has been designed to aid you when detecting and
solving possible problems with your network. These problems are
rarely serious; the cause is usually a disconnected or damaged
cable, or incorrect configuration. If this section does not solve
your problem, contact your supplier for information on what to
do next.
Perform these actions first:
• Ensure all network equipment is powered on.
• Power each piece of network equipment off, wait about five
seconds and then power each one on.
NOTE:
Do not power the Switch off and then immediately on. Wait about
five seconds between power cycles.
Check the following symptoms and solutions:
Power Status Logo not lit.
This is probably because the switch does not have power. Check
the following:
• Make sure the power lead from the power adapter is properly
connected and the cord is not damaged.
• Ensure the power adapter is correctly fitted into the power
outlet socket and that the socket switch is turned on if
applicable.
• Ensure you are using only the power adapter supplied with
the switch.
Port Status LED not lit for a port that has a TP cable connected.
After connection, it may take several seconds for the Port Status
LEDs to illuminate. The Port Status LED should turn Blue, for each
port that is connected.
If the Port Status LED is not lit after several seconds, ensure that
the connected device is powered on, that the TP cable is not
damaged and that it is correctly inserted at both ends.
You may find that a TP cable works when connected to the
Switch, but does not work if disconnected from the Switch and
connected to another device. This may be because the other
device does not have the automatic MDI/MDIX feature.
The Port Status LED is lit but the network performance of the
switch is poor.
The switch supports full-duplex autonegotiation. If the connected
device does not support autonegotiation, ensure it is configured
for half duplex operation only.
How Your Switch Can Be Used
Switching Overview
When a network of repeater hubs is in operation, any information
that is sent by the workstation is passed around the whole network
(regardless of the destination of the information). This can result
in a lot of unnecessary traffic that can slow the network down.
The Switch solves this problem because it “listens” to the network
and automatically learns what workstations can be reached
through its ports. It can then selectively pass on any information by
transmitting the traffic from the relevant port only. This operation is
called “switching”.
The Switch effectively divides up your network, localizing the
network traffic and passing on traffic as necessary. If you have any
high performance workstations that require a lot of bandwidth,
connect them directly to the Switch.
Traffic Prioritization (Gigabit Switch Only)
The Switch has a built in feature to aid network performance at
times of excessive load. It is called Priority Queuing. When a
packet is received, the Switch will examine it to see if it has been
priority encoded. If it has, the Switch will then read the priority
level and determine whether it should be directed through the
normal or high priority channel. This feature can be useful during
excessive loads, for example, when one type of traffic may require
priority over another.
Expanding Your Network
You can increase the number of workstations and other devices
that can connect to your network by adding switches. You can
connect a 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX or 1000BASE-T to each port of
the Switch.
The Switch has automatic MDI/MDIX. Simply plug in the cable,
and the Switch will automatically detect which wiring practice has
been followed, and will compensate accordingly.
Checking Unit Connections
When you have connected all your units, power on the units and
the Switch. The Port Status LEDs for the ports you have used should
be lit. If they are not, check your connections.
Hew
lett-P
ackar
d
3000 H
anov
er S
t.
Palo A
lto, CA 9
430
4, U
.S.A.
Cop
yrigh
t © 2011 H
ew
lett-P
ackar
d Com
pany. A
ll righ
ts res
erv
ed.
Mic
ros
oft, M
S-DO
S and Windo
ws ar
e regis
ter
ed trade
marks o
f
Mico
rso
ft C
orpo
rati
on.
All o
ther co
mpan
y and produ
ct name
s may be tr
ademar
ks of the
ir
res
pectiv
e com
panies
.
Par
t No: 599
8-22
74
Published: Ma
y 2011
Connecting 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX/1000BASE-T
Networks
The ports can each be connected to an Ethernet network. If you
have various connection speeds in your network, you can join
them together using the Switch allowing all your workstations
to communicate. For example, by connecting one of the ports
to a server, all the workstations connected to the server can
communicate with devices connected to the Switch, significantly
increasing the size of your network.
NOTE:
The Fast Ethernet Switch models can be used to connect to
1000BASE-T (Gigabit) networks.However, the speed of connection between
the Fast Ethernet Switch and the 1000BASE-T network will operate at 100
Mbps. Ensure that the 1000BASE-T network equipment is configured for
auto-negotiation to ensure the link operates correctly.
1
3
2
*5
99
8-
22
74
*
599
8-22
74




















