341
Task Command
Display BGP VPNv6 peer information.
display
bgp
[
instance
instance-name
]
peer
vpnv6
[
ipv4-address
mask-length
|
{
ipv4-address
|
group-name
group-name
}
log-info
| [
ipv4-address
]
verbose
]
Display BGP VPNv6 routes.
display bgp
[
instance
instance-name
]
routing-table vpnv6
[ [
route-distinguisher
route-distinguisher
] [
ipv6-address
prefix-length
[
advertise-info
] |
as-path-acl
as-path-acl-number
|
community-list
{
{
basic-community-list-number
|
comm-list-name
} [
whole-match
] |
adv-community-list-number
} ]
|
peer
ipv4-address
{
advertised-routes
|
received-routes
}
[
ipv6-address
prefix-length
|
statistics
] |
statistics
]
Display incoming labels for all BGP
VPNv6 routes.
display bgp
[
instance
instance-name
]
routing-table vpnv6
inlabel
Display outgoing labels for all BGP
VPNv6 routes.
display bgp
[
instance
instance-name
]
routing-table vpnv6
outlabel
Display BGP VPNv6 address family
update group information.
display bgp
[
instance
instance-name
]
update-group vpnv6
[
ipv4-address
]
Display OSPFv3 sham link information.
display ospfv3
[
process-id
] [
area
area-id
]
sham-link
[
verbose
]
For more information about the
display ipv6 routing-table
,
display
bgp
group
vpnv6
,
display
bgp peer vpnv6
, and
display bgp update-group vpnv6
commands, see
Layer 3—IP Routing
Command Reference
.
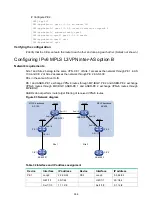
IPv6 MPLS L3VPN configuration examples
Configuring IPv6 MPLS L3VPNs
Network requirements
CE 1 and CE 3 belong to VPN 1. CE 2 and CE 4 belong to VPN 2.
VPN 1 uses route target attributes 111:1. VPN 2 uses route target attributes 222:2. Users of different
VPNs cannot access each other.
Run EBGP between CEs and PEs to exchange VPN routing information.
PEs use OSPF to communicate with each other and use MP-IBGP to exchange VPN routing
information.