22
6.
When the MPLS Forwarding State Holding timer expires, the GR restarter deletes all stale
MPLS forwarding entries.
7.
When the LDP Recovery timer expires, the GR helper deletes all stale FEC-label mappings.
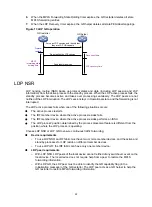
Figure 13 LDP GR operation
LDP NSR
LDP nonstop routing (NSR) backs up protocol states and data (including LDP session and LSP
information) from the active process to the standby process. When the LDP active process fails, the
standby process becomes active and takes over processing seamlessly. The LDP peers are not
notified of the LDP interruption. The LDP session stays in Operational state, and the forwarding is not
interrupted.
The LDP active process fails when one of the following situations occurs:
•
The active process restarts.
•
The IRF member device where the active process resides fails.
•
The IRF member device where the active process resides performs an ISSU.
•
The LDP process' position determined by the process placement feature is different from the
position where the LDP process is operating.
Choose LDP NSR or LDP GR to ensure continuous traffic forwarding.
•
Device
requirements
{
To use LDP NSR, an IRF fabric must have two or more member devices, and the active and
standby processes for LDP reside on different member devices.
{
To use LDP GR, the IRF fabric can have only one member device.
•
LDP peer requirements
{
With LDP NSR, LDP peers of the local device are not notified of any switchover event on the
local device. The local device does not require help from a peer to restore the MPLS
forwarding information.
{
With LDP GR, the LDP peer must be able to identify the GR capability flag (in the
Initialization message) of the GR restarter. The LDP peer acts as a GR helper to help the
GR restarter to restore MPLS forwarding information.
GR restarter
GR helper
Send label mappings
Set up an LDP session, and identify that
they are LDP GR capable
Protocol
restarts
MPLS
forwarding state
holding time
Reconnect time
LDP recovery time
Re-establish the LDP session