24
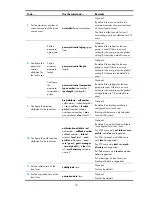
To set the username format and the traffic statistics units for a RADIUS scheme:
To do…
Use the command…
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
—
2.
Enter RADIUS scheme view.
radius scheme
radius-scheme-
name
—
3.
Set the format for usernames
sent to the RADIUS servers.
user-name-format
{
keep-original
|
with-domain
|
without-domain
}
Optional.
By default, the ISP domain name
is included in a username.
4.
Specify the unit for data flows
or packets sent to the RADIUS
servers.
data-flow-format
{
data
{
byte
|
giga-byte
|
kilo-byte
|
mega-byte
}
|
packet
{
giga-packet
|
kilo-
packet
|
mega-packet
|
one-
packet
} }*
Optional.
It is set to
byte
for data flows and
one-packet
for data packets by
default.
If a RADIUS scheme defines that the username is sent without the ISP domain name, do not apply the
RADIUS scheme to more than one ISP domain. Otherwise, users who are using the same username but
are in different ISP domains are considered to be the same user.
For level switching authentication, the
user-name-format keep-original
and
user-name-format without-
domain
commands produce the same results: they make sure that usernames sent to the RADIUS server
carry no ISP domain name.
Setting the supported RADIUS server type
The supported RADIUS server type determines the type of the RADIUS protocol that the switch uses to
communicate with the RADIUS server. It can be standard or extended:
•
Standard
—Uses the standard RADIUS protocol, compliant to RFC 2865 and RFC 2866 or later.
•
Extended
—Uses the proprietary RADIUS protocol of HP.
When the RADIUS server runs iMC, you must set the RADIUS server type to
extended
. When the RADIUS
server runs third-party RADIUS server software, either RADIUS server type applies. For the switch to
function as a RADIUS server to authenticate login users, you must set the RADIUS server type to
standard
.
To set the RADIUS server type:
To do…
Use the command…
Remarks
1.
Enter system view.
system-view
—
2.
Enter RADIUS scheme view.
radius scheme
radius-scheme-
name
—
3.
Set the RADIUS server type.
server-type
{
extended
|
standard
}
Optional.
It is set to
standard
by default.
Changing the RADIUS server type restores the unit for data flows and that for packets that are sent to the
RADIUS server to the defaults.
Setting the maximum number of RADIUS request transmission attempts
Because RADIUS uses UDP packets to transfer data, the communication process is not reliable. RADIUS
uses a retransmission mechanism to improve the reliability. If a NAS sends a RADIUS request to a
RADIUS server but receives no response after the response timeout timer (defined by the
timer response-
timeout
command) expires, it retransmits the request. If the number of transmission attempts exceeds the