51
Tunnel ID: Invalid Interface: Ethernet1/1
BkTunnel ID: Invalid BkInterface: N/A
# Display routes destined for 100.1.1.0/24 on Router B when the link between Router A and
Router B fails.
<RouterB> display ip routing-table 100.1.1.0 24 verbose
Summary Count : 1
Destination: 100.1.1.0/24
Protocol: RIP Process ID: 1
SubProtID: 0x1 Age: 00h21m23s
Cost: 4 Preference: 100
Tag: 0 State: Active Adv
OrigTblID: 0x0 OrigVrf: default-vrf
TableID: 0x2 OrigAs: 0
NBRID: 0x12000003 LastAs: 0
AttrID: 0xffffffff Neighbor: 192.168.3.2
Flags: 0x1008c OrigNextHop: 192.168.3.2
Label: NULL RealNextHop: 192.168.3.2
BkLabel: NULL BkNextHop: N/A
Tunnel ID: Invalid Interface: Ethernet1/2
BkTunnel ID: Invalid BkInterface: N/A
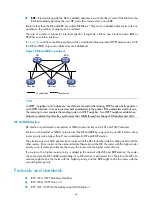
Configuring BFD for RIP (bidirectional control detection)
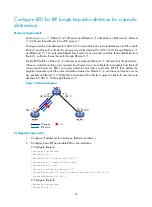
Network requirements
As shown in
, Ethernet 1/2 of Router A and Ethernet 1/1 of Router C run RIP process 1. Ethernet
1/1 on Router A runs RIP process 2. Ethernet 1/2 on Router C, and Ethernet 1/1 and Ethernet 1/2 on
Router D run RIP process 1.
Configure a static route destined for 100.1.1.0/24 on Router A, configure a static route destined for
101.1.1.0/24 on Router C, and enable static route redistribution into RIP on Router A and Router C so
Router A can learn two routes destined for 100.1.1.0/24 through Ethernet 1/2 and Ethernet 1/1,
respectively, and uses the one through Ethernet 1/2.
Enable BFD for RIP on Ethernet 1/2 of Router A and Ethernet 1/1 of Router C. When the link over
Ethernet 1/2 fails, BFD can quickly detect the link failure and notify RIP so RIP deletes the neighbor
relationship and the route information learned on Ethernet 1/2, and uses the route destined for
100.1.1.0/24 through Ethernet 1/1.