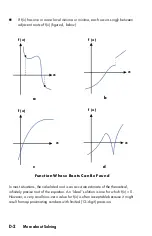
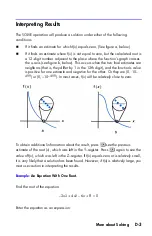
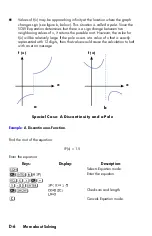
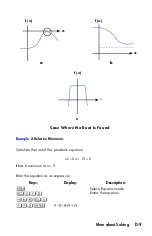
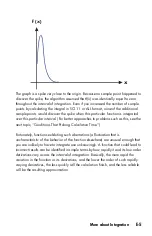
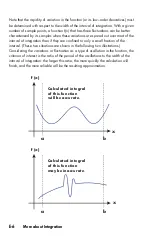
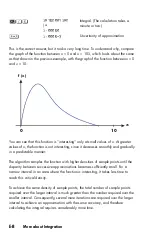
D-13
Solve for X using initial guesses of 10
–8
and –10
–8
.
Round–Off Error
The limited (12–digit) precision of the calculator can cause errors due to rounding
off, which adversely affect the iterative solutions of SOLVE and integration. For
example,
has no roots because
f(x)
is always greater than zero. However, given initial guesses
of 1 and 2, SOLVE returns the answer 1.0000 due to round–off error.
Round–off error can also cause SOLVE to fail to find a root. The equation
has a root at
. However, no 12–digit number
exactly
equals
, so the
calculator can never make the function equal to zero. Furthermore, the function
never changes sign SOLVE returns the message
.
Keys:
(In RPN mode)
Display:
Description:
X
_
Enters guesses.
J
Selects program "J" as the function.
X
Solves for
X
; displays the result.
0
10
-
]
10
1)
x
[(
30
2
15
=
+
+
0
7
-
x
2
=
7
7
Summary of Contents for 35s
Page 1: ...HP 35s scientific calculator user s guide H Edition 1 HP part number F2215AA 90001 ...
Page 14: ...12 Contents ...
Page 15: ...Part 1 Basic Operation ...
Page 16: ......
Page 46: ...1 30 Getting Started ...
Page 63: ...RPN The Automatic Memory Stack 2 17 A Solution ...
Page 64: ...2 18 RPN The Automatic Memory Stack ...
Page 74: ...3 10 Storing Data into Variables ...
Page 180: ...12 14 Statistical Operations ...
Page 181: ...Part 2 Programming ...
Page 182: ......
Page 246: ...15 12 Solving and Integrating Programs ...
Page 270: ...16 24 Statistics Programs ...
Page 284: ...17 14 Miscellaneous Programs and Equations ...
Page 285: ...Part 3 Appendixes and Reference ...
Page 286: ......
Page 308: ...B 8 User Memory and the Stack ...
Page 322: ...C 14 ALG Summary ...
Page 336: ...D 14 More about Solving ...
Page 346: ...E 10 More about Integration ...
Page 352: ...F 6 Messages ...
Page 370: ...G 18 Operation Index ...
Page 382: ...Index 12 ...