Storage Management Overview
46
NAS 2000s Administration Guide
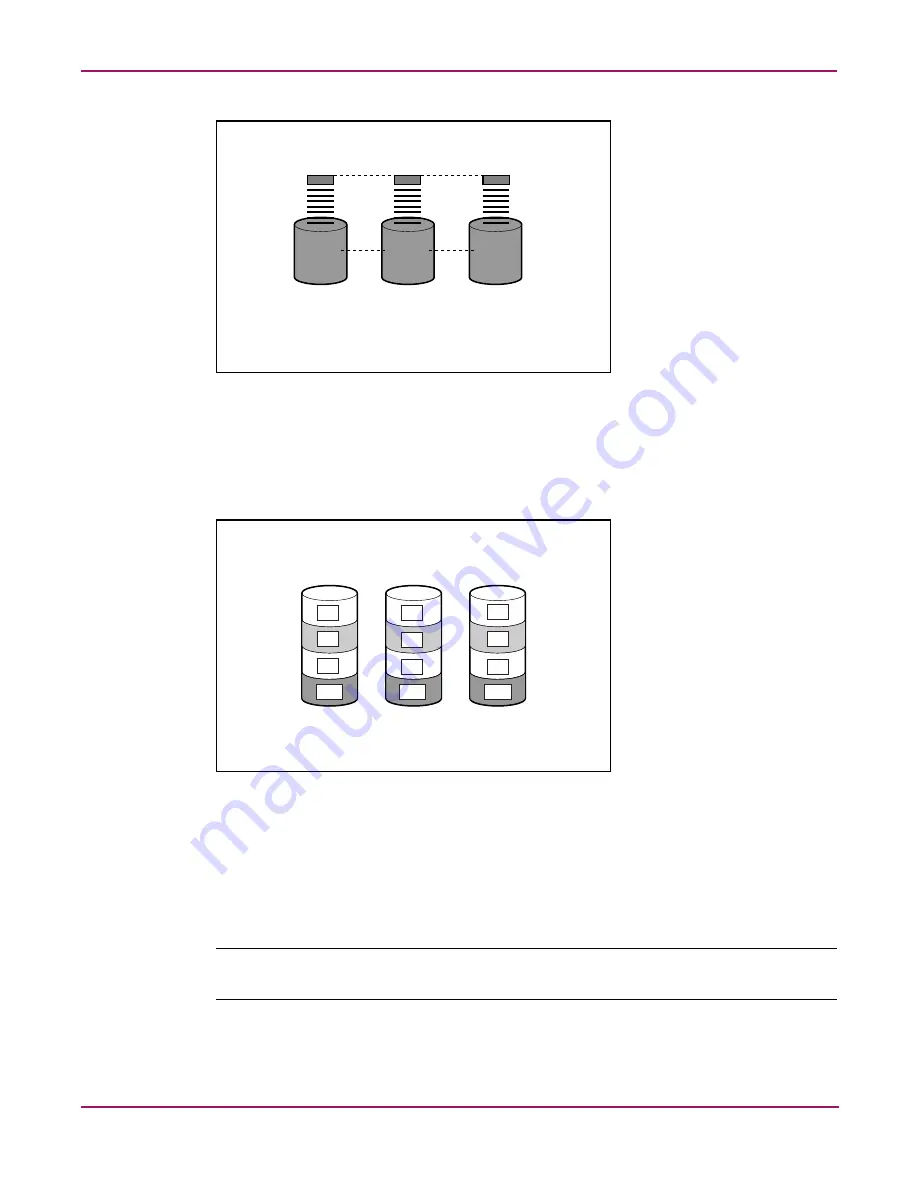
Figure 21: Configuring the physical drives into an array dramatically improves read/write
efficiency
Because the read/write heads are active simultaneously, the same amount of data is written to
each drive during any given time interval. Each unit of data is termed a block. The blocks form
a set of data stripes over all the hard drives in an array, as shown in
Figure 22: RAID 0 (data striping) (S1-S4) of data blocks (B1-B12)
For data in the array to be readable, the data block sequence within each stripe must be the
same. This sequencing process is performed by the array controller, which sends the data
blocks to the drive write heads in the correct order.
A natural consequence of the striping process is that each hard drive in a given array will
contain the same number of data blocks.
Note:
If one hard drive has a larger capacity than other hard drives in the same array, the extra
capacity is wasted because it cannot be used by the array.
L1
P1
P2
P3
S1
S2
S3
S4
B1
B4
B7
B2
B5
B8
B11
B10
B12
B6
B3
B9
Summary of Contents for 345646-001 - StorageWorks NAS 2000s External Storage Server
Page 16: ...About this Guide 16 NAS 2000s Administration Guide ...
Page 56: ...Storage Management Overview 56 NAS 2000s Administration Guide ...
Page 80: ...Disk Management 80 NAS 2000s Administration Guide ...
Page 110: ...User and Group Management 110 NAS 2000s Administration Guide ...
Page 146: ...Folder Printer and Share Management 146 NAS 2000s Administration Guide ...
Page 186: ...NetWare File System Management 186 NAS 2000s Administration Guide ...
















































