Honeywell
Parameter Descriptions
79
10
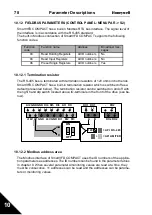
10.12.3 Modbus process data
Process data is an address area for fieldbus control. Fieldbus control is active when
the value of parameter 2.1 (Control place) is 3 (=fieldbus). The contents of the pro-
cess data has been determined in the application. The following tables present the
process data contents in the General Purpose Application.
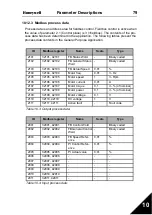
ID
Modbus register
Name
Scale
Type
2101
32101, 42101
FB Status Word
-
Binary coded
2102
32102, 42102
FB General Status
Word
-
Binary coded
2103
32103, 42103
FB Actual Speed
0,01
%
2104
32104, 42104
Motor freq.
0,01
+/- Hz
2105
32105, 42105
Motor speed
1
+/- Rpm
2106
32106, 42106
Motor current
0,01
A
2107
32107, 42107
Motor torque
0,1
+/- % (of nominal)
2108
32108, 42108
Motor power
0,1
+/- % (of nominal)
2109
32109, 42109
Motor voltage
0,1
V
2110
32110, 42110
DC voltage
1
V
2111
32111, 42111
Active fault
-
Fault code
Table 10.3: Output process data:
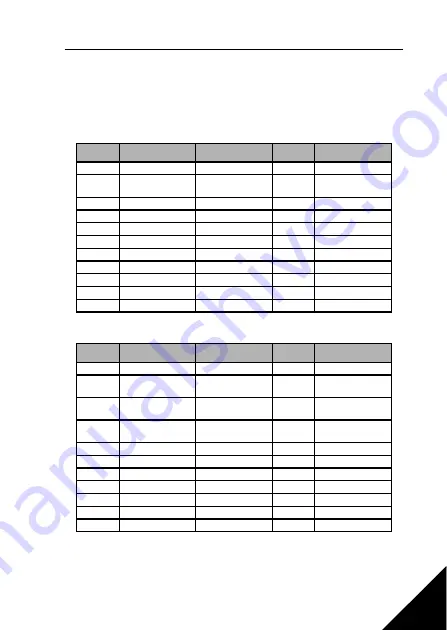
ID
Modbus register
Name
Scale
Type
2001
32001, 42001
FB Control Word
-
Binary coded
2002
32002, 42002
FB General Control
Word
-
Binary coded
2003
32003, 42003
FB Speed Refer-
ence
0,01
%
2004
32004, 42004
PI Control Refer-
ence
0,01
%
2005
32005, 42005
PI Actual value
0,01
%
2006
32006, 42006
-
-
-
2007
32007, 42007
-
-
-
2008
32008, 42008
-
-
-
2009
32009, 42009
-
-
-
2010
32010, 42010
-
-
-
2011
32011, 42011
-
-
-
Table 10.4: Input process data: