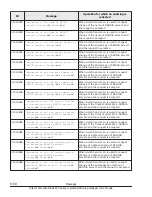
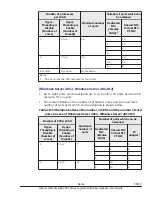
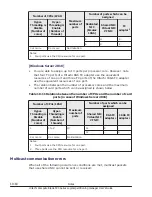
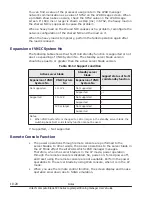
Memory allocation to LPARs
Memory setting over 1TB is supported only for the following OSs. Do not set
it to other OS, otherwise OSs might not boot properly.
•
Windows Server 2008 R2 *1
•
Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
•
Windows Server 2012
•
Windows Server 2012 R2
•
Windows Server 2016
•
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6
•
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7
*1: When using a memory in excess of 1TB, you must set the memory by
following procedures.
1
.
Set the memory capacity to less than 1TB, and boot the OS.
2
.
Apply the KB980598 into the OS.
3
.
Shut down the OS.
4
.
Set the memory capacity to over 1TB, and boot the OS.
PCI Device Assignment
•
When LPAR using a USB device is changed, the connection target of the
remote console is changed together.
•
It is necessary to assign the USB device to the LPAR which uses the USB
device before activation. You cannot select an LPAR, to which the USB
device is not assigned, to use the USB device.
•
It is necessary to activate an LPAR to use the USB device. You cannot
select the LPAR deactivated or in failure to use the USB device. When the
LPAR using a USB device fails, you cannot change the destination of the
USB device to another LPAR.
•
Check carefully that the condition is as described below, and detach the
USB device.
– The OS is not in the booting or rebooting.
– USB device is recognized by the OS or firmware for use once, and then
the USB device is detached from the OS by performing hardware secure
detachment for Windows or unmount operation for Linux.
– Do not remain to lock Alt, Windows, Ctrl and Shift keys after display
the Remote console.
If detaching the USB device when these conditions are not met, the
following phenomena might occur.
– Unstable status in firmware or OS, or OS hang up.
– Data loss or remaining the display of the USB device on the OS.
– Keyboard operation does not worked correctly.
When these phenomena above occur by detaching the USB device, carry
out the procedure corresponding to each phenomenon.
10-8
Notes
Hitachi Compute Blade 500 Series Logical partitioning manager User's Guide