L3 cache allocation functionality
Overview of the L3 cache allocation functionality
You can use the L3 cache allocation functionality to divide the L3 cache
among multiple LPARs and allocate part of the divided cache to each LPAR.
This functionality uses Cache Allocation Technology (CAT), which is provided
as part of Intel Resource Director Technology (RDT).
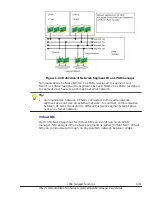
If, for example, you operate an LPAR that requires response performance
(web server) and an LPAR that puts a high load on the memory (database) at
the same time, data of the LPAR (web server) might be forced out from the
L3 cache, and degradation or variance in response performance might occur.
You can prevent such degradation or variance in response performance by
using the L3 cache allocation functionality to secure the L3 cache space
required for the LPAR (web server).
By default, the entire L3 cache is allocated to each LPAR, but you can
dynamically change the size of the L3 cache space that is allocated to each
LAPR. Note, however, that you can change the L3 cache allocation only for
LPARs to which processors have been allocated in dedicated mode.
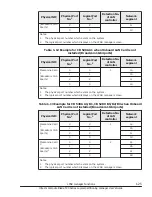
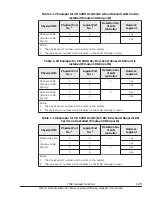
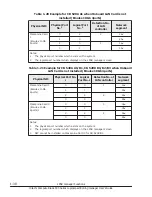
You can allocate L3 cache space to LPARs by using the capacity bit mask
(CBM) format (a mask value format). By using a CBM, you can specify not
only the size of the L3 cache space to be allocated to LPARs, but also detailed
settings such as the distance and overlapping of L3 cache allocation among
LPARs. Each specified CBM value must be in the range of the implemented bit
width of the CBM and must be a combination of consecutive ones (1). For
example, if the implemented bit width of the CBM is 20, FFFFFh, 0FF00h, and
0003Ch are acceptable, but values such as 10001h, 00100h, and 0F0F0h are
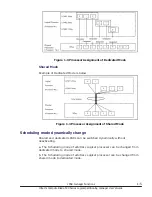
not acceptable. As shown below, there are three possible combinations of
CBMs for multiple LPARs. In the following figure, the implemented bit width of
CBMs is 8.
1-18
LPAR manager Functions
Hitachi Compute Blade 500 Series Logical partitioning manager User's Guide