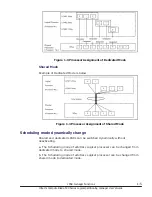
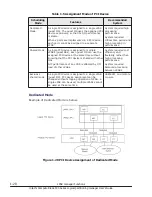
Figure 1-8 Idle Detection
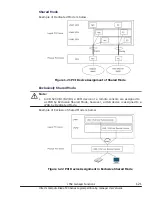
Processor Capping
With the processor capping function on, the shared mode LPAR does not take
on the unused (idle) capacity of other LPARs even if the LPAR requires more
performance than its allocation rate (busy status). Therefore, the LPAR's
processor-time never uses more processor-time the allocation rate, even if it
is busy. However, because the LPAR manager allocation rate control allows a
tolerance of 1% for each unit of processor-time, a shared mode LPAR is
allocated a maximum processor-time that is 1% greater than the total service
time of the physical processors assigned to it, and may exceed the allocation
rate.
Note that the processor capping function does not affect the execution of the
dedicated mode LPARs. Also processor capping has a meaning only to LPAR of
shared mode. Processor capping does not have any meaning to LPAR of
dedicated mode, and it cannot assign.
Figure 1-9 Processor Capping
1-8
LPAR manager Functions
Hitachi Compute Blade 500 Series Logical partitioning manager User's Guide