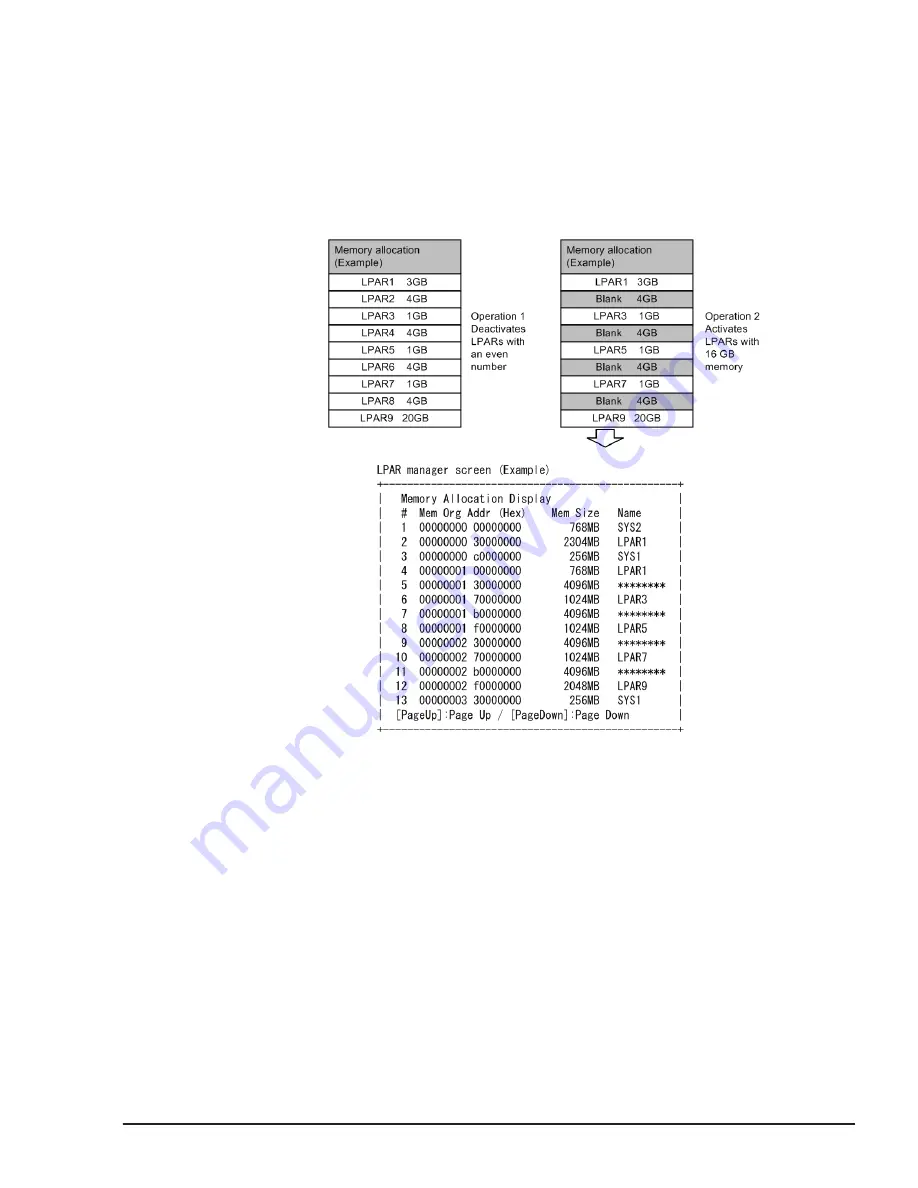
Example 2:
Failure in LPAR activation due to LPAR memory fragmentation
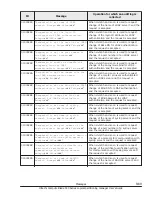
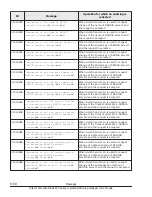
(LPAR activation fails when 4 or more discontinuous blanks of memory which
all the blanks are under the following condition are allocated to an LPAR)
Condition: Blank size exceeds the total memory size from the row which
physical memory address is "00000000 00000000" to the row above the row
which 'Name' column is 'SYS1' on "Memory Allocation Display" (*1).
Figure 10-2 Example 2 of Memory Fragmentation
When this problem has occurred, performing the following operations may
activate the LPAR. You can find the LPAR memory allocation on the physical
memory in the memory allocation display in the logical partition (LPAR)
configuration screen.
1
.
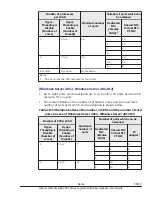
The size of memory which allocate to activated LPAR is set to the size
under the total memory size from the row which physical memory
address is "00000000 00000000" to the row above the row which Name
column is SYS1 on Memory Allocation Display.
2
.
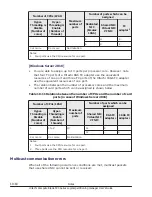
Deactivate an LPAR which the memory next to blank memory is allocated
to in order to reduce the number of discontinuous blank of memory.
3
.
Define a dummy LPAR, set the memory size of the dummy LPAR to the
total memory size which shown at 1.).
Notes
10-7
Hitachi Compute Blade 500 Series Logical partitioning manager User's Guide