Logical Partitioning of Processors
The method of logically dividing the physical processor is referred to as the
scheduling mode. You can select dedicated mode or shared mode for the
scheduling mode. Different features of each mode are shown in the table
below.
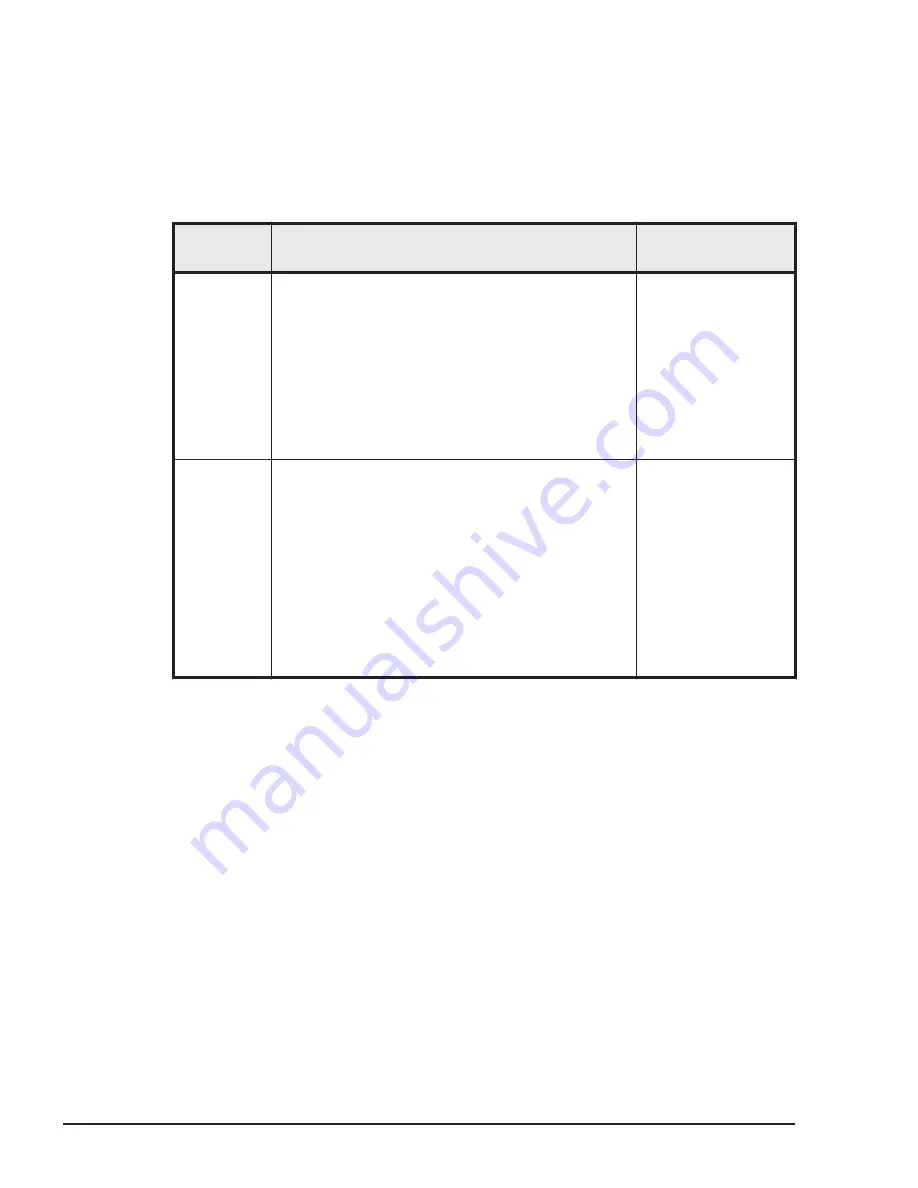
Table 1-3 Processor Scheduling Mode
Mode
Description
Recommended
System
Dedicated
Mode
•
The logical processor on an LPAR dedicatedly
uses the corresponding physical processor.
•
Since there is no overhead for switching the
physical processors between the logical
processors, the LPAR performs faster.
•
For each LPAR, it is possible to specify the
number of dedicated logical processors
assigned. (However, it is not possible to specify
more than the number of physical processors
available.)
•
System required
high processing
performance
•
System required
critical time
period and high
processing in
performance
Shared
Mode
•
Physical processors are time-shared among the
logical processors defined in the LPAR for which
the shared mode is specified.
•
The utilization rate of the physical processors
can be set dynamically for each LPAR, allowing
flexible use of physical processor resources.
•
The number of logical processors to be used in
the shared mode can be set for each LPAR. (It
is possible to specify more than the number of
physical processors available, but this
operations may cause the extremely slow
down.)
•
System required
cost efficiency
and flexibility
rather than high
processing
performance
•
System required
balanced
processing
between LPARs
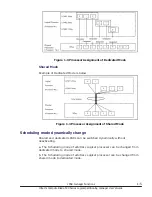
Dedicated Mode
Example of Dedicated Mode is below
1-4
LPAR manager Functions
Hitachi Compute Blade 500 Series Logical partitioning manager User's Guide