26
Ethernet Configuration
cally (dynamically), a DHCP server (English DHCP beco-
mes; Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is required for
the dispatching of IP addresses. With a DHCP server an IP
address range for the automatic dispatching of IP addres-
ses can be preset. A DHCP server is usually already inte-
grated in a router (DSL router, ISDN router, Modem router,
WLAN router, …) integrated. If a network element (e.g.
an instrument) is connected by a network cable directly
with a host (PC), the IP addresses cannot be assigned to
the instrument and the host (PC) automatically, since no
network with DHCP server is present here. They have to
be preset therefore at the instrument and at the host (PC)
manually.
IP addresses are divided by using subnet mask into a
network quota and into a host quota, so similarly e.g. a
telephone number is divided in pre selection (land and
local area network number) and call number (user number).
Subnet mask have the same form as IP addresses. They are
represented with four decimal numbers separated by points
(e.g. 255.255.255.0). As is the case for the IP addresses here
each decimal number represents a binary number of 8 bits.
The separation between network quota and host quota
is determined by the subnet mask within an IP address
(e.g. the IP address 192.168.10.10 by the subnet mask
255.255.255.0 is divided into a network quota 192.168.10.0
and a host quota of 0.0.0.10). The allocation takes place via
the transformation of the IP address and the subnet mask
in binary form and afterwards a bit by bit one logical AND
operation between IP address and subnet mask. The result
is the network quota of the IP address. The host quota of
the IP address takes place via the bit by bit logical NAND
operation between IP address and subnet mask. By the
variable allocation of IP addresses in network quota and
host quota via subnet masks, one can specify IP address
ranges individually for large and small networks. Thus one
can operate large and small IP networks and connect if ne-
cessary to the Internet via a router. In smaller local networks
the subnet mask 255.255.255.0 is mostly used. Network
quota (the first 3 numbers) and host quota (the last number)
are simple here without much mathematical expenditure to
determine and it can with these subnet mask up to 254 net-
work elements (e.g. measuring instruments, hosts/PC‘s...) in
a network be operated at the same time.
Often also a standard gateway is present in a network. In
most local networks is this gateway with the router to the
Internet (DSL router, ISDN router, …) …) is identical. Using
this (gateway -) router a connection can be manufactured
with another network. Thus also network elements, which
are not in the same (local) network, can be reached and/
or network elements from the local network are able to ex-
change data with network elements from other networks.
For a network-spreading data exchange the IP address
of the standard gateway must also be preset. In local
networks, mostly the first IP address within a network for
this (gateway -) router is used. Mostly routers in a local
network to be used as gateway have an IP address with a
„1“ in the last place of the IP address (e.g. 192.168.10.1).
5.2 Different instruments of Hameg
Please refer to the manual of the appropriate Hameg
instrument for information about activating the desired
interface and which interface parameters have to be set.
5.3 Ethernet interface parameters at the host (PC)
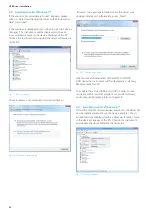
Windows XP™ parameters
To preset the interface parameters of the Ethernet LAN
interface at the host PC please open the “Start“ menu
and select “Control Panel“ --
>
„Network connections“ --
>
“Local Area Connection“. In the new opened window “Lo-
cal Area Connection Properties“ please click on “Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP)“ and “Properties“.
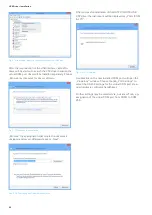
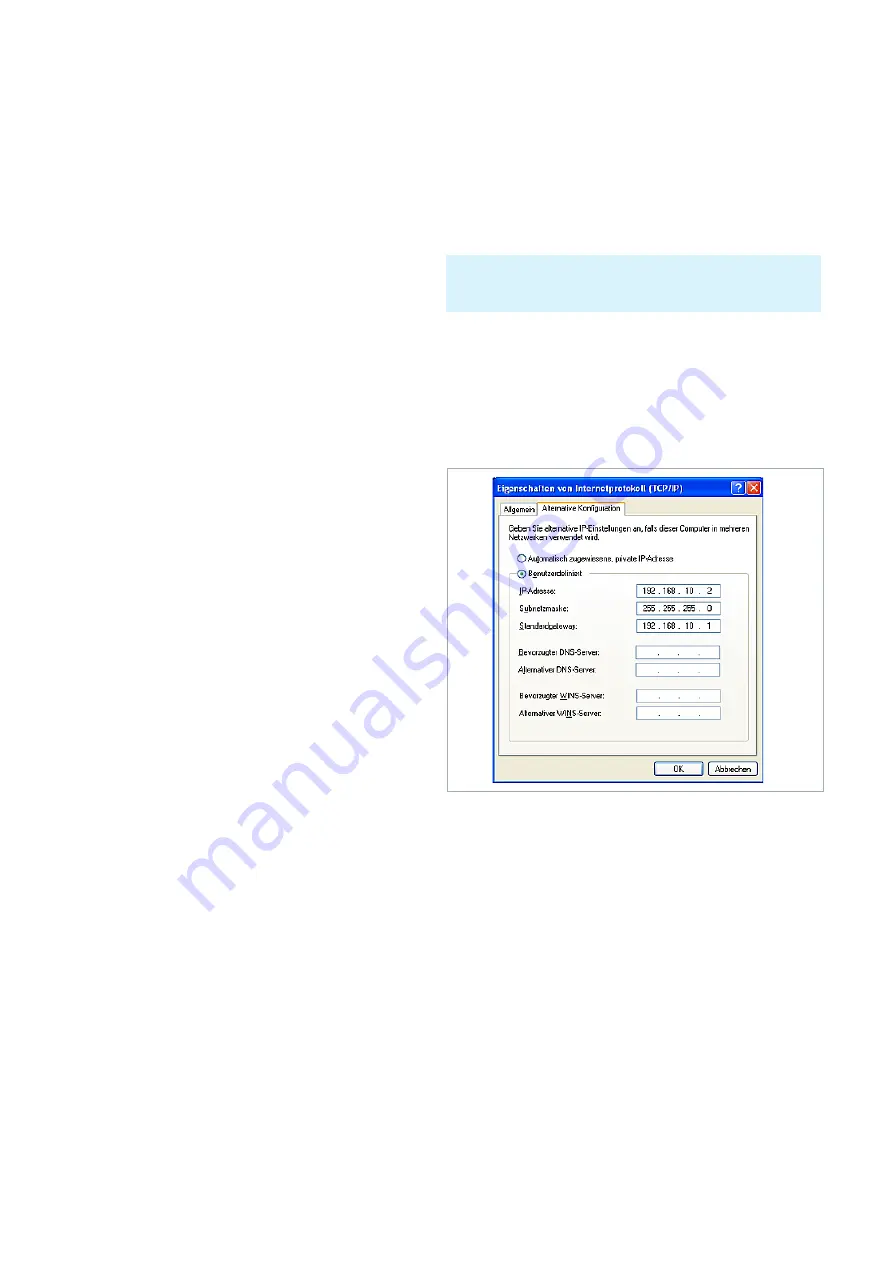
In the new opened window “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties“ please click on “Alternative Configuration“ and
select the option “User configured“ for the manual preset
of the network parameters.
❙ In the input field „IP adress“ enter your (or from a
network administrator specified) IP address of the PC
(e.g. 192.168.10.2).
❙ In the input field “Subnet mask“ enter your (or from a
network administrator specified) subnet mask of the PC
(e.g. 255.255.255.0).
❙ In the input field “Default gateway“ enter your (or from a
network administrator specified) IP address of the
gateway (e.g. the IP address of the router of its LAN
network).
❙
If you connect the host (PC) and the Instrument via
network cable directly, this setting is optional.
In order to accomplish the following parameters, you need admi-
nistrator rights at the host (PC) or you have to be member of the
user group “administrators“ (e.g. in the network).
Fig. 5.2: Characteristics of the Internet protocol