8
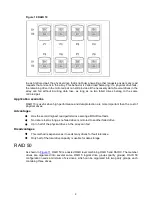
Figure 9 RAID 6
Application scenarios
RAID 6 is most useful when data loss is unacceptable, but cost is also an important factor. Data loss
is less likely to occur in an array configured with RAID 6 than an array configured with RAID 5.
Advantages
•
Has a high read performance.
•
Has high data availability because any two drives can fail without loss of critical data.
•
More drive capacity is usable than with RAID 10 because parity information requires only the
storage space equivalent to two physical drives.
Disadvantages
The main disadvantage of RAID 6 is a relatively low write performance (lower than RAID 5),
because of the need for two sets of parity data.
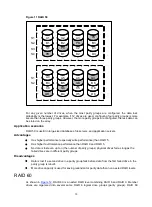
RAID 10
, RAID 10 is a nested RAID level combining RAID 1 and RAID 0. To configure
RAID 10, first configure RAID 1 and then RAID 0.
Summary of Contents for UniServer E3200 G3
Page 35: ...19 Figure 29 Selecting the RAID volume to be deleted...
Page 116: ...56 Figure 96 Controller Configuration screen...
Page 220: ...61 Figure 109 Selecting Main Menu 2 Select Controller Management and press Enter...
Page 243: ...84 Figure 153 Confirming the operation...
Page 293: ...50 Figure 89 Clearing completion...
Page 382: ...21 Figure 27 Storage controller information...
Page 389: ...7 Figure 8 Identifying a storage controller 2...