Intel Rapid Start Technology
A. System Requirements
Windows 7 with SP1
1.
An SSD with size larger than the total system memory
2.
Intel Rapid Start Technology enabled in BIOS Setup
3.
AHCI/RAID mode supported (please note if the SSD has been assigned as a member of a RAID array, it
4.
cannot be used to set up Intel Rapid Start store partition); IDE mode not supported
All motherboard drivers correctly installed
5.
B. Creating a Primary Store Partition
Below it is assumed Windows 7 is already installed on the SATA hard drive.
Open Disk Management Tool
Step 1: Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Administrative Tools > Computer Management >Storage
> Disk Management.
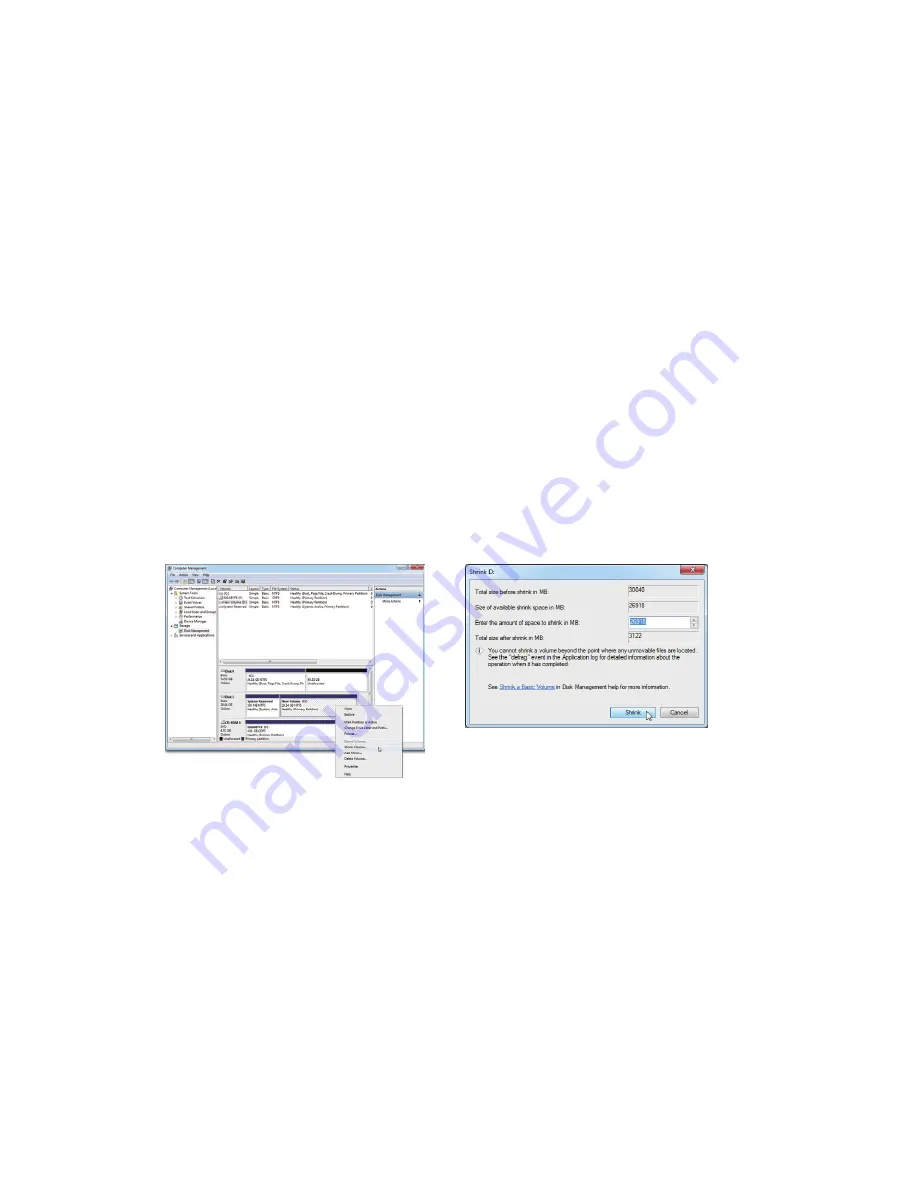
Step 2: Select the SSD on which you want to create the store partition (if the SSD is unallocated, create a
new partition first), and right-click on the partition you select and select
Shrink Volume
. (Figure 1)
Step 3: Enter the size of the required partition (it should be at least equal to the size of the memory
currently installed on the system. (1 GB=1024 MB. For example, to set 8 GB, enter 8192 MB). The
recommendation is to create a partition equal to the maximum memory capacity supported on the
system, in order to take care of future memory upgrade scenarios.)
Step 4: When completed, click
Shrink
. (Figure 2)
C. Launching DiskPart Disk Partitioning Tool to Set up Intel Rapid Start Store Partition
Open the command prompt window and run diskpart.exe (enter "
diskpart
" at the C:\> command prompt
and press <Enter>). At the diskpart prompt, type the following commands in sequence. Note: The commands for
MBR format and GPT format are different. Refer to the commands below. After entering all of the commands,
be sure to restart your computer.
MBR format:
DISKPART>list disk
(Lists the disks and information about them)
DISKPART>select disk X
(Selects a disk. "
X
" is the disk number where you
want to create the store partition. Refer to results from
"
list disk
" for the exact disk number)
DISKPART>create partition primary
(Create the primary store partition)
Figure 2
Figure 1






