GE Healthcare
Senographe DS
Revision 1
Service Information and Procedures Class A 2385072-16-8EN
Job Card ELE A032 – IQ Tools Flat Field Test
Page no. 699
Chapter 7
JC-ELE-A-032.fm
Job Card ELE A032 – IQ Tools Flat Field Test
Chapter 7
1
SUPPLIES
None
2
APPLICABILITY
This Job Card applies to the core product. If the system has the CESM option, perform the CESM ver-
sion of this Job Card located in the CESM IM/SIP instead.
3
TOOLS
•
•
(16 cells Nuclear Associates 18-220 or RMI-156)
4
REQUIRED EFFORT
Personnel: 1 Field Engineer
Time: 30 minutes.
5
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
The procedures in this Job Card produce X-rays. Ensure that you take appropriate precautions when
operating with X-rays (for example, stay behind the radiation screen during an X-ray exposure).
6
PREREQUISITES
The system must have been correctly installed and calibrated.
7
FLATFIELD TESTS
7-1
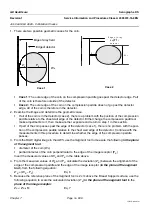
Objective
The flatfield test measures the ability of the detector to reproduce the image of a flat and homogeneous
phantom.
The ideal response of the detector is a uniform image with no large or small defects, with no pixel having
a signal much higher or much weaker than its neighbors, and with a uniform signal-to-noise ratio. The
quantities to look for are thus:
-
Brightness Non uniformity
: the magnitude of low frequency structures (large shapes).
-
High frequency modulatio
n: the magnitude of high frequency structures (small defects).
-
Number and density of bad pixels
: the number of pixels having signals significantly different
from those of their neighbors (new bad pixels appeared since the latest bad pixel calibration), and
the density of these bad pixels.
-
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) Non uniformity
: the variation of signal-to-noise ratio over the
image.
A test failure indicates incorrect test conditions (phantom position, cleanliness), or an artifact causing
inconsistency between the current image and the associated gain map. Such an inconsistency means
that either the gain calibration needs to be updated, or the current image contains a defect which must
be identified (see section
). Possible sources of artifacts include the tube output window, the mirror, the
Molybdenum filter, the collimator blades, and the detector.