5
RESIDUAL OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION
On a healthy three-phase power system, the sum of the three-phase to earth voltages is nominally zero, as it is the
vector sum of three balanced vectors displaced from each other by 120°. However, when an earth fault occurs on
the primary system, this balance is upset and a residual voltage is produced. This condition causes a rise in the
neutral voltage with respect to earth. Consequently this type of protection is also commonly referred to as 'Neutral
Voltage Displacement' or NVD for short.
This residual voltage may be derived (from the phase voltages) or measured (from a measurement class open
delta VT). Derived values will normally only be used where the model does not support measured functionality (a
dedicated measurement class VT). If a measurement class VT is used to produce a measured Residual Voltage, it
cannot be used for other features such as Check Synchronisation.
This offers an alternative means of earth fault detection, which does not require any measurement of current. This
may be particularly advantageous in high impedance earthed or insulated systems, where the provision of core
balanced current transformers on each feeder may be either impractical, or uneconomic, or for providing earth
fault protection for devices with no current transformers.
5.1
RESIDUAL OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION IMPLEMENTATION
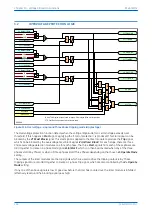
Residual Overvoltage Protection is implemented in the RESIDUAL O/V NVD column of the relevant settings group.
Some applications require more than one stage. For example an insulated system may require an alarm stage and
a trip stage. It is common in such a case for the system to be designed to withstand the associated healthy phase
overvoltages for a number of hours following an earth fault. In such applications, an alarm is generated soon after
the condition is detected, which serves to indicate the presence of an earth fault on the system. This gives time for
system operators to locate and isolate the fault. The second stage of the protection can issue a trip signal if the
fault condition persists.
The product provides two stages of Residual Overvoltage protection with independent time delay characteristics.
Stage 1 provides a choice of operate characteristics, where you can select between:
●
An IDMT characteristic
●
DT (Definite Time)
The IDMT characteristic is defined by the following formula:
t = K/( M - 1)
where:
●
K= Time multiplier setting
●
t = Operating time in seconds
●
M = Derived residual voltage setting voltage (VN> Voltage Set)
You set this using the VN>1 Function setting.
Stage 1 also provides a Timer Hold facility.
Stage 2 can have definite time characteristics only. This is set in the VN>2 status cell
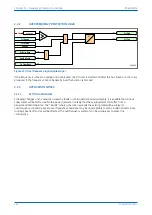
The device derives the residual voltage internally from the three-phase voltage inputs supplied from either a 5-limb
VT or three single-phase VTs. These types of VT design provide a path for the residual flux and consequently permit
the device to derive the required residual voltage. In addition, the primary star point of the VT must be earthed.
Three-limb VTs have no path for residual flux and are therefore unsuitable for this type of protection.
P54A/B/C/E
Chapter 10 - Voltage Protection Functions
P54xMED-TM-EN-1
231
Summary of Contents for P4A
Page 2: ......
Page 20: ...Contents P54A B C E xviii P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 27: ...CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ...
Page 28: ...Chapter 1 Introduction P54A B C E 2 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 38: ...Chapter 1 Introduction P54A B C E 12 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 39: ...CHAPTER 2 SAFETY INFORMATION ...
Page 40: ...Chapter 2 Safety Information P54A B C E 14 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 52: ...Chapter 2 Safety Information P54A B C E 26 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 53: ...CHAPTER 3 HARDWARE DESIGN ...
Page 54: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design P54A B C E 28 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 86: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design P54A B C E 60 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 87: ...CHAPTER 4 SOFTWARE DESIGN ...
Page 88: ...Chapter 4 Software Design P54A B C E 62 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 99: ...CHAPTER 5 CONFIGURATION ...
Page 100: ...Chapter 5 Configuration P54A B C E 74 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 120: ...Chapter 5 Configuration P54A B C E 94 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 121: ...CHAPTER 6 CURRENT DIFFERENTIAL PROTECTION ...
Page 122: ...Chapter 6 Current Differential Protection P54A B C E 96 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 149: ...CHAPTER 7 AUTORECLOSE ...
Page 150: ...Chapter 7 Autoreclose P54A B C E 124 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 207: ...CHAPTER 8 CB FAIL PROTECTION ...
Page 208: ...Chapter 8 CB Fail Protection P54A B C E 182 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 219: ...CHAPTER 9 CURRENT PROTECTION FUNCTIONS ...
Page 220: ...Chapter 9 Current Protection Functions P54A B C E 194 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 244: ...Chapter 9 Current Protection Functions P54A B C E 218 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 247: ...CHAPTER 10 VOLTAGE PROTECTION FUNCTIONS ...
Page 248: ...Chapter 10 Voltage Protection Functions P54A B C E 222 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 261: ...CHAPTER 11 FREQUENCY PROTECTION FUNCTIONS ...
Page 262: ...Chapter 11 Frequency Protection Functions P54A B C E 236 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 268: ...Chapter 11 Frequency Protection Functions P54A B C E 242 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 269: ...CHAPTER 12 MONITORING AND CONTROL ...
Page 270: ...Chapter 12 Monitoring and Control P54A B C E 244 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 300: ...Chapter 12 Monitoring and Control P54A B C E 274 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 301: ...CHAPTER 13 SUPERVISION ...
Page 302: ...Chapter 13 Supervision P54A B C E 276 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 312: ...Chapter 13 Supervision P54A B C E 286 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 323: ...CHAPTER 14 DIGITAL I O AND PSL CONFIGURATION ...
Page 324: ...Chapter 14 Digital I O and PSL Configuration P54A B C E 298 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 336: ...Chapter 14 Digital I O and PSL Configuration P54A B C E 310 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 337: ...CHAPTER 15 FIBRE TELEPROTECTION ...
Page 338: ...Chapter 15 Fibre Teleprotection P54A B C E 312 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 354: ...Chapter 15 Fibre Teleprotection P54A B C E 328 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 355: ...CHAPTER 16 ELECTRICAL TELEPROTECTION ...
Page 356: ...Chapter 16 Electrical Teleprotection P54A B C E 330 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 366: ...Chapter 16 Electrical Teleprotection P54A B C E 340 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 367: ...CHAPTER 17 COMMUNICATIONS ...
Page 368: ...Chapter 17 Communications P54A B C E 342 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 439: ...CHAPTER 18 CYBER SECURITY ...
Page 440: ...Chapter 18 Cyber Security P54A B C E 414 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 457: ...CHAPTER 19 INSTALLATION ...
Page 458: ...Chapter 19 Installation P54A B C E 432 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 471: ...CHAPTER 20 COMMISSIONING INSTRUCTIONS ...
Page 472: ...Chapter 20 Commissioning Instructions P54A B C E 446 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 513: ...CHAPTER 21 MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING ...
Page 514: ...Chapter 21 Maintenance and Troubleshooting P54A B C E 488 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 530: ...Chapter 21 Maintenance and Troubleshooting P54A B C E 504 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 531: ...CHAPTER 22 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS ...
Page 532: ...Chapter 22 Technical Specifications P54A B C E 506 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 558: ...Chapter 22 Technical Specifications P54A B C E 532 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 559: ...APPENDIX A ORDERING OPTIONS ...
Page 560: ...Appendix A Ordering Options P54A B C E P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 565: ...APPENDIX B SETTINGS AND SIGNALS ...
Page 566: ...Appendix B Settings and Signals P54A B C E P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 790: ...Appendix B Settings and Signals P54A B C E B224 P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 835: ...APPENDIX C WIRING DIAGRAMS ...
Page 836: ...Appendix C Wiring Diagrams P54A B C E P54xMED TM EN 1 ...
Page 849: ......