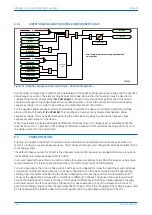
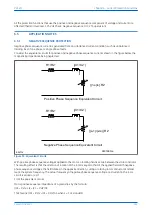
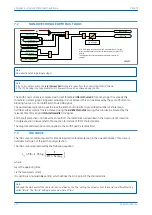
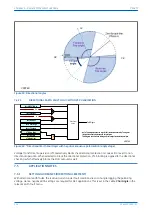
V00641
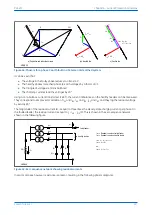
a) capacitive and inductive currents with resistive components
N
b) Unfaulted line
c) Faulted line
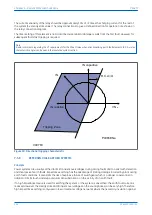
Operate
Restrain
Zero torque line for 0° RCA
Zero torque line for 0° RCA
Operate
Restrain
I’
L
Resistive component
in grounding coil
Resistive component
in feeder
(I
AH1
+ I
H2
+ I
H3
)’
3V
0
B
C
A
-I
H 1
- I
H2
I
L
I
R1
= I
H1
I
R 3
I
R3
= I
F
+ I
H3
= I
L
- I
H1
- I
H12
V
res
= -3V
0
V
res
= -3V
0
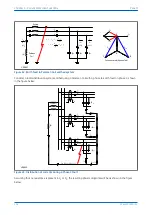
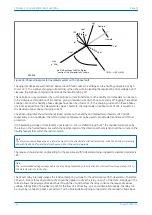
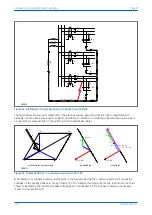
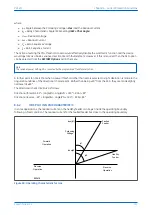
Figure 46: Phase C earth fault in Petersen Coil earthed system: practical case with resistance present
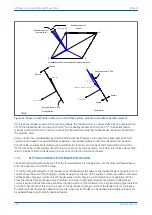
If the residual voltage is used as the polarising voltage, the residual current is phase shifted by an angle less than
90° on the faulted feeder, and greater than 90° on the healthy feeders. With an RCA of 0°, the healthy feeder
residual current will fall in the ‘restrain’ area of the characteristic while the faulted feeder residual current falls in
the ‘operate’ area.
Often, a resistance is deliberately inserted in parallel with the Petersen Coil to ensure a measurable earth fault
current and increase the angular difference between the residual signals to reinforce the directional decision.
Directionality is usually implemented using a Wattmetric function, or a transient earth fault detection function
(TEFD), rather than a simple directional function, since they are more sensitive. For further information about TEFD,
refer to Transient Earth Fault Detection in the Current Protection Functions chapter.
7.5.3
SETTING GUIDELINES (COMPENSATED NETWORKS)
The directional setting should be such that the forward direction is looking down into the protected feeder (away
from the busbar), with a 0° RCA setting.
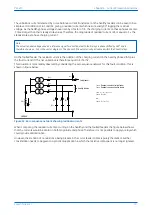
For a fully compensated system, the residual current detected by the relay on the faulted feeder is equal to the coil
current minus the sum of the charging currents flowing from the rest of the system. Further, the addition of the two
healthy phase charging currents on each feeder gives a total charging current which has a magnitude of three
times the steady state per phase value. Therefore, for a fully compensated system, the detected unbalanced
current is equal to three times the per phase charging current of the faulted circuit. A typical setting may therefore
be in the order of 30% of this value, i.e. equal to the per phase charging current of the faulted circuit. In practise,
the exact settings may well be determined on site, where system faults can be applied and suitable settings can
be adopted based on practically obtained results.
Chapter 6 - Current Protection Functions
P24xM
118
P24xM-TM-EN-2.1
Summary of Contents for P24DM
Page 2: ......
Page 17: ...Appendix C Wiring Diagrams 467 P24xM Contents P24xM TM EN 2 1 xv...
Page 18: ...Contents P24xM xvi P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 24: ...Table of Figures P24xM xxii P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 25: ...CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION...
Page 26: ...Chapter 1 Introduction P24xM 2 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 37: ...CHAPTER 2 SAFETY INFORMATION...
Page 38: ...Chapter 2 Safety Information P24xM 14 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 51: ...CHAPTER 3 HARDWARE DESIGN...
Page 52: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design P24xM 28 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 66: ...Chapter 3 Hardware Design P24xM 42 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 67: ...CHAPTER 4 SOFTWARE DESIGN...
Page 68: ...Chapter 4 Software Design P24xM 44 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 77: ...CHAPTER 5 CONFIGURATION...
Page 78: ...Chapter 5 Configuration P24xM 54 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 94: ...Chapter 5 Configuration P24xM 70 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 95: ...CHAPTER 6 CURRENT PROTECTION FUNCTIONS...
Page 96: ...Chapter 6 Current Protection Functions P24xM 72 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 188: ...Chapter 6 Current Protection Functions P24xM 164 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 189: ...CHAPTER 7 RESTRICTED EARTH FAULT PROTECTION...
Page 190: ...Chapter 7 Restricted Earth Fault Protection P24xM 166 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 201: ...CHAPTER 8 CB FAIL PROTECTION...
Page 202: ...Chapter 8 CB Fail Protection P24xM 178 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 215: ...CHAPTER 9 CURRENT TRANSFORMER REQUIREMENTS...
Page 216: ...Chapter 9 Current Transformer Requirements P24xM 192 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 224: ...Chapter 9 Current Transformer Requirements P24xM 200 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 225: ...CHAPTER 10 VOLTAGE PROTECTION FUNCTIONS...
Page 226: ...Chapter 10 Voltage Protection Functions P24xM 202 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 245: ...CHAPTER 11 FREQUENCY PROTECTION FUNCTIONS...
Page 246: ...Chapter 11 Frequency Protection Functions P24xM 222 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 261: ...CHAPTER 12 POWER PROTECTION FUNCTIONS...
Page 262: ...Chapter 12 Power Protection Functions P24xM 238 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 265: ...CHAPTER 13 MONITORING AND CONTROL...
Page 266: ...Chapter 13 Monitoring and Control P24xM 242 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 294: ...Chapter 13 Monitoring and Control P24xM 270 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 295: ...CHAPTER 14 SUPERVISION...
Page 296: ...Chapter 14 Supervision P24xM 272 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 312: ...Chapter 14 Supervision P24xM 288 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 313: ...CHAPTER 15 DIGITAL I O AND PSL CONFIGURATION...
Page 314: ...Chapter 15 Digital I O and PSL Configuration P24xM 290 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 327: ...CHAPTER 16 COMMUNICATIONS...
Page 328: ...Chapter 16 Communications P24xM 304 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 386: ...Chapter 16 Communications P24xM 362 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 387: ...CHAPTER 17 CYBER SECURITY...
Page 388: ...Chapter 17 Cyber Security P24xM 364 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 405: ...CHAPTER 18 INSTALLATION...
Page 406: ...Chapter 18 Installation P24xM 382 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 419: ...CHAPTER 19 COMMISSIONING INSTRUCTIONS...
Page 420: ...Chapter 19 Commissioning Instructions P24xM 396 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 443: ...CHAPTER 20 MAINTENANCE AND TROUBLESHOOTING...
Page 444: ...Chapter 20 Maintenance and Troubleshooting P24xM 420 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 453: ...CHAPTER 21 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS...
Page 454: ...Chapter 21 Technical Specifications P24xM 430 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 486: ...Chapter 21 Technical Specifications P24xM 462 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 487: ...APPENDIX A ORDERING OPTIONS...
Page 488: ...Appendix A Ordering Options P24xM 464 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 491: ...APPENDIX B SETTINGS AND SIGNALS...
Page 493: ...APPENDIX C WIRING DIAGRAMS...
Page 494: ...Appendix C Wiring Diagrams P24xM 468 P24xM TM EN 2 1...
Page 497: ......
Page 498: ......
Page 499: ......
Page 500: ......
Page 501: ......
Page 502: ......
Page 503: ......
Page 504: ......
Page 505: ......
Page 506: ......
Page 507: ......
Page 508: ......
Page 509: ......
Page 510: ......
Page 511: ......
Page 512: ......
Page 513: ......
Page 514: ......
Page 515: ......
Page 516: ......
Page 517: ......
Page 518: ......
Page 519: ......
Page 520: ......
Page 521: ......
Page 522: ......
Page 523: ......
Page 524: ......
Page 525: ......
Page 526: ......
Page 527: ......
Page 528: ......
Page 529: ......
Page 530: ......
Page 531: ......
Page 532: ......
Page 533: ......
Page 534: ......
Page 535: ......
Page 536: ......
Page 537: ......
Page 538: ......
Page 539: ......
Page 540: ......
Page 541: ......
Page 542: ......
Page 543: ......
Page 544: ......
Page 545: ......
Page 546: ......
Page 547: ......
Page 548: ......
Page 549: ......
Page 550: ......
Page 551: ......
Page 552: ......
Page 553: ......
Page 554: ......
Page 555: ......
Page 556: ......
Page 557: ......
Page 558: ......
Page 559: ......
Page 560: ......
Page 561: ......
Page 562: ......
Page 563: ......
Page 564: ......
Page 565: ......
Page 566: ......
Page 567: ......
Page 568: ......
Page 569: ......
Page 570: ......
Page 571: ......
Page 572: ......
Page 573: ......
Page 574: ......
Page 575: ......
Page 576: ......
Page 577: ......
Page 578: ......
Page 579: ......
Page 580: ......
Page 581: ......
Page 582: ......
Page 583: ......
Page 584: ......
Page 585: ......
Page 586: ......
Page 587: ......
Page 588: ......
Page 589: ......
Page 590: ......
Page 591: ......
Page 592: ......
Page 593: ......
Page 594: ......
Page 595: ......
Page 596: ......
Page 597: ......
Page 598: ......
Page 599: ......