GE Multilin
L30 Line Current Differential System
9-5
9 THEORY OF OPERATION
9.1 OVERVIEW
9
(EQ 9.15)
The 87G restraining signal is calculated as follows:
(EQ 9.16)
The terms for the second remote terminal are omitted in two-terminal applications.
The operate signal for the ground differential function,
, is then calculated as:
(EQ 9.17)
The restraint signal,
,
is calculated as follows for two-terminal applications:
(EQ 9.18)
The restraint signal,
,
is calculated as follows for three-terminal applications:
(EQ 9.19)
where
is the slope setting for the ground differential function.
The ground differential element picks up if the following condition holds.
(EQ 9.20)
where
is the pickup setting for the ground differential function.
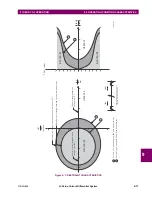
In other words, when the squared magnitude of the operating signal is greater than the total restraining squared signal, the
element operates. For additional security, the function is blocked if the restraining signal is high, indicating the 87LG func-
tion is not required to clear high-current faults, allowing for more sensitive settings to be used for the 87LG function.
9.1.8 CLOCK SYNCHRONIZATION
Synchronization of data sampling clocks is needed in a digital differential protection scheme, because measurements must
be made at the same time. Synchronization errors show up as phase angle and transient errors in phasor measurements at
the terminals. By phase angle errors, we mean that identical currents produce phasors with different phase angles. By tran-
sient errors, we mean that when currents change at the same time, the effect is seen at different times at different measure-
ment points. For best results, samples should be taken simultaneously at all terminals.
In the case of peer to peer architecture, synchronization is accomplished by synchronizing the clocks to each other rather
than to a master clock. Each relay compares the phase of its clock to the phase of the other clocks and compares the fre-
quency of its clock to the power system frequency and makes appropriate adjustments. The frequency and phase tracking
algorithm keeps the measurements at all relays within a plus or minus 25 microsecond error during normal conditions for a
2 or 3 terminal system. For 4 or more terminals the error may be somewhat higher, depending on the quality of the commu-
nications channels. The algorithm is unconditionally stable. In the case of 2 and 3 terminal systems, asymmetric communi-
cations channel delay is automatically compensated for. In all cases, an estimate of phase error is computed and used to
automatically adapt the restraint region to compensate. Frequency tracking is provided that will accommodate any fre-
quency shift normally encountered in power systems.
If
I
REM_REST_A
2
BP
2
, then
I
REM_REST_A
2
I
REM_RESTRAINT_A
2
4
3
---
S
1
2
-----------------------------------------------------
=
else
I
REM_REST_A
2
I
REM_RESTRAINT_A
2
4
3
---
S
1
BP
2
–
4
3
---
S
2
2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
BP
2
+
=
I
RES_87G
2
max
I
LOC_REST_A
2
I
LOC_REST_B
2
I
LOC_REST_C
2
I
REM1_REST_A
2
I
REM1_REST_B
2
=
I
REM1_REST_C
2
I
REM2_REST_A
2
I
REM2_REST_B
2
I
REM2_REST_C
2
I
OP_87G
2
I
OP_87G
2
I
OP_87G_RE
2
I
OP_87G_IM
2
+
=
I
87G
2
I
87G
2
2
S
87G
2
I
RES_87G
2
=
I
87G
2
I
87G
2
4
3
---
S
87G
2
I
RES_87G
2
=
S
87G
I
OP_87G
2
2
P
87G
2
I
87G
2
+
–
0
and
I
RES_87G
2
3 pu
2
P
87G
Summary of Contents for L30
Page 10: ...x L30 Line Current Differential System GE Multilin TABLE OF CONTENTS ...
Page 30: ...1 20 L30 Line Current Differential System GE Multilin 1 5 USING THE RELAY 1 GETTING STARTED 1 ...
Page 370: ...5 244 L30 Line Current Differential System GE Multilin 5 10 TESTING 5 SETTINGS 5 ...
Page 464: ...A 10 L30 Line Current Differential System GE Multilin A 1 PARAMETER LISTS APPENDIX A A ...
Page 600: ...C 30 L30 Line Current Differential System GE Multilin C 7 LOGICAL NODES APPENDIX C C ...
Page 610: ...D 10 L30 Line Current Differential System GE Multilin D 1 IEC 60870 5 104 APPENDIX D D ...
Page 622: ...E 12 L30 Line Current Differential System GE Multilin E 2 DNP POINT LISTS APPENDIX E E ...
Page 634: ...F 12 L30 Line Current Differential System GE Multilin F 3 WARRANTY APPENDIX F F ...
Page 644: ...x L30 Line Current Differential System GE Multilin INDEX ...