Radar Interpretation
Reading and interpreting the radar display takes practice.
The more you use the radar, the better you will become at
relying on the radar display when you really need it.
Radar can be useful in many situations, such as avoiding
collisions when you have limited visibility, for example
when it is dark or foggy, tracking weather, seeing what
is ahead of you, and locating birds and fish.
The radar overlay feature can help you interpret the
radar display more easily, because it overlays the radar
returns on top of the chart. This can help you identify
the difference between a radar return of a land mass,
bridge, or rain cloud. Showing the AIS vessels on the
radar overlay can also help you identify features on the
radar display.
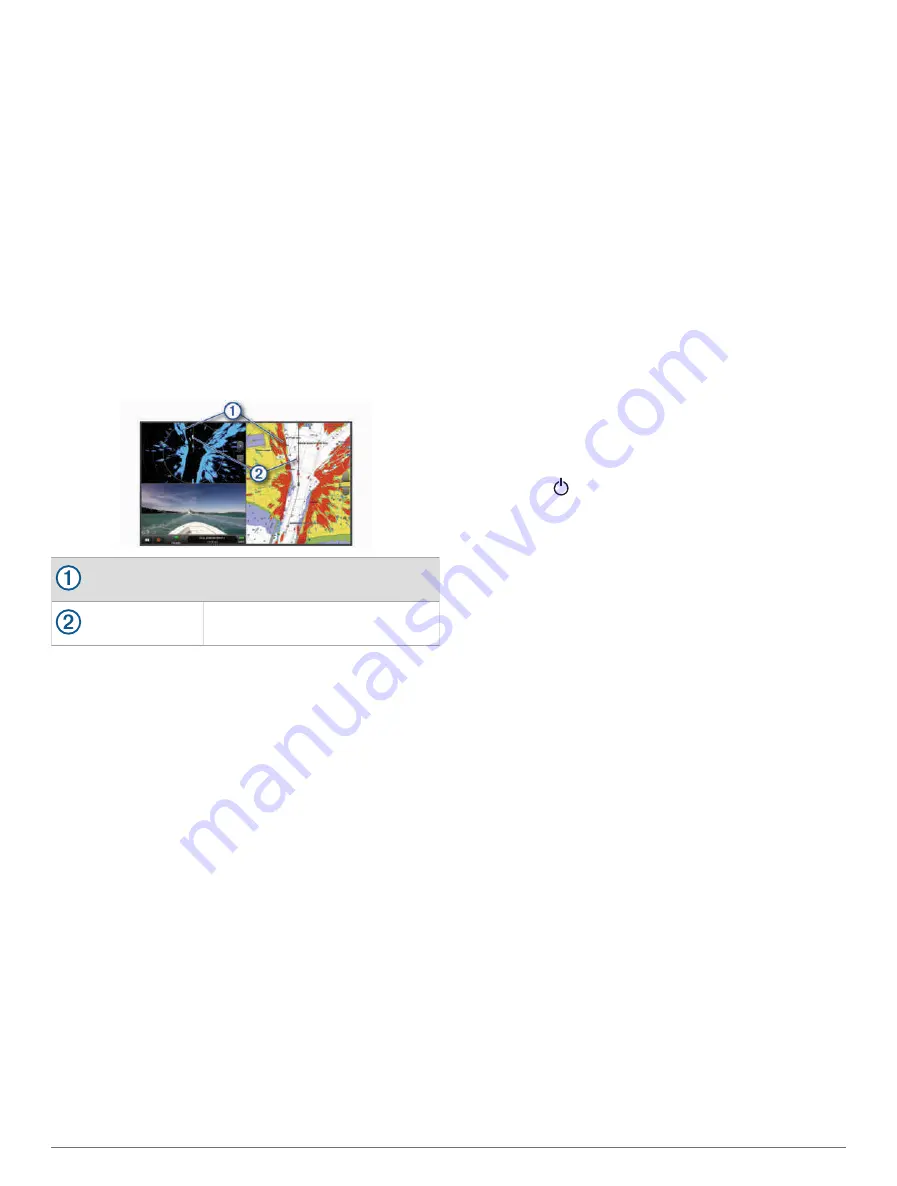
In the screenshot below, the radar overlay is turned on.
This screen also shows a video feed. We can easily
identify a few items on the radar screen.
Land
Vessel
Radar Overlay
When you connect your chartplotter to an optional Garmin
marine radar, you can use overlay radar information on
the Navigation chart or on the Fishing chart.
Data appears on the radar overlay based on the most
recently used radar mode and all settings configurations
applied to the radar overlay are also applied to the last-
used radar mode.
Radar Overlay and Chart Data Alignment
When using the Radar overlay, the chartplotter aligns
radar data with chart data based on the boat heading,
which is based by default on data from a magnetic
heading sensor connected using a NMEA
®
0183 or NMEA
2000 network. If a heading sensor is not available, the
boat heading is based on GPS tracking data.
GPS tracking data indicates the direction in which the boat
is moving, not the direction in which the boat is pointing. If
the boat is drifting backward or sideways due to a current
or wind, the Radar overlay may not perfectly align with
the chart data. This situation should be avoided by using
boat-heading data from an electronic compass.
If the boat heading is based on data from a magnetic
heading sensor or an automatic pilot, the heading data
could be compromised due to incorrect setup, mechanical
malfunction, magnetic interference, or other factors. If the
heading data is compromised, the Radar overlay may not
align perfectly with the chart data.
Transmitting Radar Signals
NOTE:
As a safety feature, the radar enters standby mode
after it warms up. This gives you an opportunity to verify
the area around the radar is clear before beginning radar
transmission.
1
With the chartplotter off, connect your radar as
described in the radar installation instructions.
2
Turn on the chartplotter.
If necessary, the radar warms up and a countdown
alerts you when the radar is ready.
3
Select
Radar
.
4
Select a radar mode.
A countdown message appears while the radar is
starting up.
5
Select
Options
>
Transmit Radar
.
Stopping the Transmission of Radar Signals
From a radar screen, select
Options
>
Radar To
Standby
.
TIP:
Press >
Radar To Standby
from any screen to
quickly stop radar transmission.
Setting Up the Timed Transmit Mode
To help conserve power, you can set up time intervals in
which the radar will transmit and not transmit (standby)
signal transmissions.
NOTE:
This feature is not available in dual radar modes.
1
From a radar screen, select
Options
>
Radar Options
>
Timed Transmit
.
2
Select
Timed Transmit
to enable the option.
3
Select
Stdby Time
, enter the time interval between
radar signal transmissions, and select
Done
.
4
Select
Transmit Time
, enter the duration of each radar
signal transmission, and select
Done
.
Enabling and Adjusting a Radar No Transmit Zone
You can indicate areas within which the radar scanner
does not transmit signals.
NOTE:
GMR Fantom and xHD2 radar models support two
no-transmit zones. Most other GMR radar models support
one no-transmit zone. GMR 18 HD+ radar models do not
support no-transmit zones.
1
From a radar screen, select
Options
>
Radar Setup
>
Installation
>
No Transmit Zone
.
The no-transmit zone is indicated by a shaded area on
the radar screen.
2
Select
Angle 1
, and select the new location for the first
angle.
3
Select
Angle 2
, and select the new location for the
second angle.
4
Select
Done
.
5
If necessary, repeat for the second zone.
50
Radar






























