GS2011M Low Power WiFi Module Data Sheet
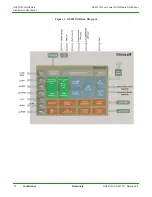
GS2011M Architecture
Wireless LAN and System Control Subsystem
GS2011M-DS-001211, Release 0.9
Confidential Preliminary
21
Wireless LAN and System Control Subsystem
The WLAN CPU subsystem consists of the WLAN CPU, its ROM, RAM, 802.11 b/g/n
MAC/PHY, and peripherals. This CPU is intended primarily to implement the 802.11 MAC
protocols. The CPU system has GPIO, Timer, and Watchdog for general use. A UART is
provided as a debug interface. A SPI interface is provided for specific application needs.
The WLAN CPU can access the RTC registers through an asynchronous AHB bridge.
WLAN CPU has only Flash read access to the on-board flash memory. The WLAN
subsystem interacts with the APP subsystem through a set of mailboxes and shared
dual–port memories.
The CPUs provide debug access through a JTAG/serial port. For GS2011 module, the
complete JTAG port is brought out for both CPUs. The CPUs also include code and data
trace and watch point logic to assist in-system debugging of SW.
The WLAN subsystem includes an integrated power amplifier, and provides management
capabilities for an optional external power amplifier. In addition, it contains hardware
support for AES-CCMP encryption (for WPA2) and RC4 encryption (for WEP & WPA
TKIP) encryption/decryption.
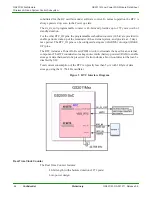
Onboard Antenna / RF Port / Radio
The GS2011Mxx modules have fully integrated RF frequency synthesizer, reference clock,
low power PA, and a high power PA (GS2011MIE) for extended range applications. Both
TX and RX chain in the module incorporate internal power control loops. The GS2011Mxx
modules also incorporate an on board antenna option plus a variety of regulatory certified
antenna options for various application needs.
802.11 MAC
The 802.11 MAC implements all time critical functionality of the 802.11b/g/n protocols. It
works in conjunction with the MAC SW running on the CPU to implement the complete
MAC functionality. It interfaces with the PHY to initiate transmit/receive and CCA. The
PHY registers are programmed indirectly through the MAC block. The MAC interfaces to
the system bus and uses DMA to fetch transmit packet data and save receive packet data.
The MAC SW exchanges packet data with the HW though packet descriptors and pointers.
Key Features
•
Compliant to IEEE 802.11 (2012)
•
Compliant to IEEE 802.11b/g/n (11n – 2009)
•
Long and short preamble generation on frame-by-frame basis for 11b frames
•
Transmit rate adaptation
•
Transmit power control
•
Frame aggregation (AMPDU, AMSDU)
•
Block ACK (Immediate, Compressed)