QUANTUM™ HD UNITY SYSTEM CONTROLLER
MAINTENANCE
090.670-M (APR 2020)
Page 29
The following pictorial shows a side view of the 120 VAC
Input module. The color of an Input module is yellow:
Figure 14: Digital input module - side view
5
-
4
+
3
+
COM OUT VDC
5VDC LOGIC
2
∼
1
90-140VAC
AC INPUT
120 VAC
Never plug a 120 V Input module into a 240 V system, and
vice-versa. Never plug an Output module into a position
designated for an Input module.
You will notice that when a module is plugged into the
Digital board, there is a fuse located directly adjacent to
the module. This fuse is of the plugable variety, and must
be plugged into the IN position for an Input module.
Digital Outputs
A Digital Output is the portion of the hardware that is used
to energize components. These devices include solenoids,
relay coils, and heaters to be energized, based upon the
logic within the Quantum™ HD Unity System Controller
software.
The following pictorial shows a side view of the 120 VAC
Output module. The color of an Output module is black:
Figure 15: Digital output module - side view
4
-
3
+
3-8 VDC
DC CONTROL
2
∼
1
3A 280VAC
AC OUTPUT
120 VAC Output
Although this Output module is labeled as 280 VAC on the
top, and on the side, it can be used on both 120 V and
240 V applications.
Never plug an Input module into a position designated for
an Output module.
You will notice that when a module is plugged into the
Digital Board, there is a fuse located directly adjacent to
the module. This fuse is of the plugable variety, and must
be plugged into the OUT position for an Output module.
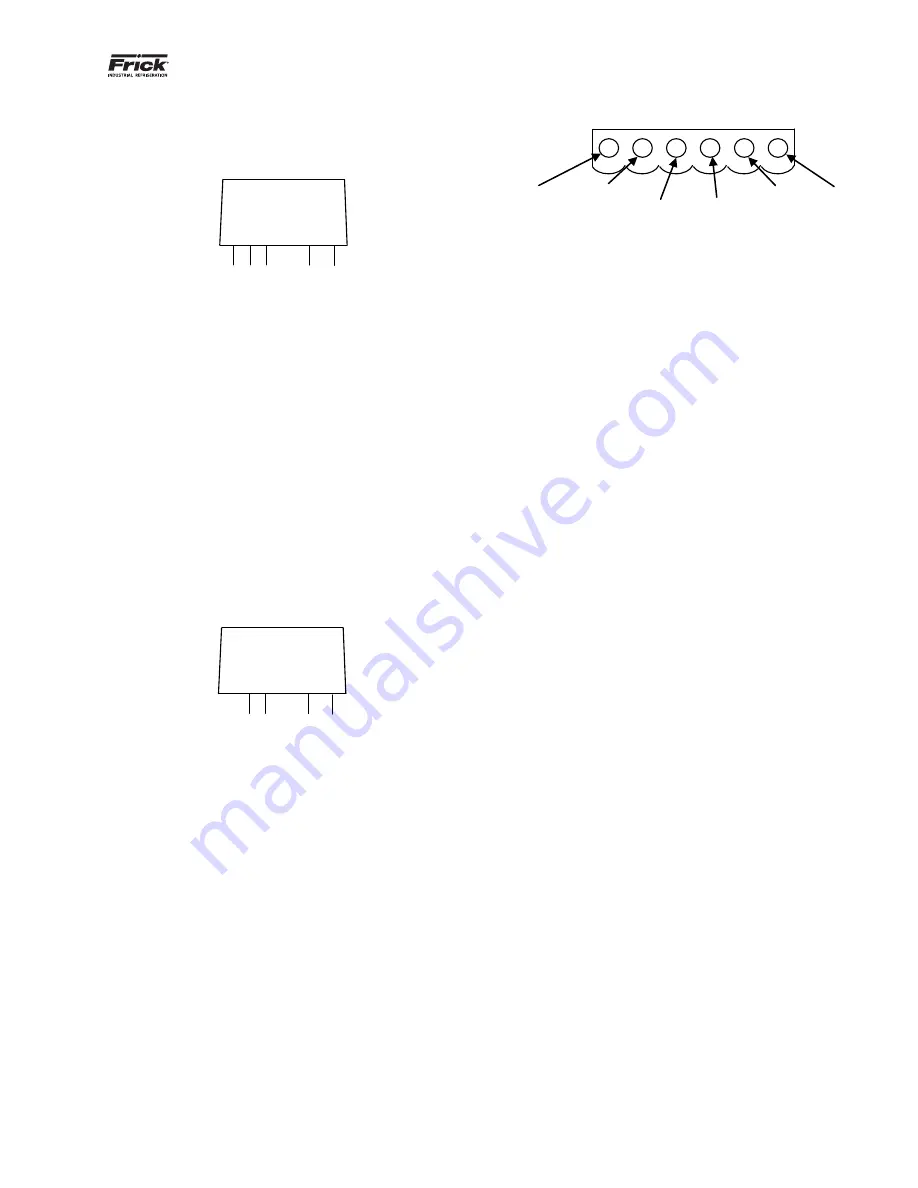
Checking the Digital Inputs and Outputs
Some problems may require troubleshooting the digital
inputs and outputs. The Digital I/O (Input / Output) Boards
have six Digital I/O (DIO) board connectors labeled P1
through P6. The Input and Output modules are wired to a
DIO connector plug. Position 3 provides power and posi-
tion 4 is a neutral on the DIO connectors. Positions 1, 2, 5,
and 6 are signal connections:
Figure 16: Signal connections
HOT
NEUTRAL
Position1
Signal
Position2
Signal
Position3
Signal
Position4
Signal
The Digital I/O board’s I/O modules are configured by
proper module selection, AC or DC, operating voltage,
input or output, and moving the fuse to the in or out posi-
tion. An LED is associated with each module and displays
the state of each module. A lit LED represents an Input
that is High, receiving a signal or an Output that is On.
If a properly configured Digital I/O is not responding cor
-
rectly, first look at the Digital Board on the Digital I/O
Screen and check if the module is on. If it is not on, check
if the LED on the Digital Board is also not lit. If the LED is
not lit, then check the fuse. If the fuse is OK, then check
the module.
Fuse Testing and Replacement
1. Power off the panel.
2. Open the panel door.
3. Remove the questionable fuse.
4. Place the questionable fuse into the fuse tester at the
one end of each Digital I/O Board. See the Digital Board
drawings at the end of this section for exact fuse tester
location.
5. Power on the panel.
6. Check the LED on the tester. If the LED is lit, the fuse
is OK.
7. Power off the panel.
8. If the fuse is faulty, check for external shorts on the
corresponding circuit. Replace the fuse with a new
plug-type fuse; see
Recommended Spare Parts
list.
9. If the panel cannot be powered down to do the on-
board fuse test, a simple continuity test can be per-
formed using a DVM.
Input and Output Module Testing and
Replacement
1. Power off the panel.
2. Open the panel door.
3. Replace the questionable module.
4. Power on the panel.
5. If it is an Output module, check for proper panel volt-
age on the DIO connector plug. Check the voltage be-
tween position 4 (neutral) and the associated position
to the Output module.
6. If it is an Input module, check if the associated LED is
on when power is applied to the module.






























