2
Product description
30
Festo – GDCP-CMMO-ST-EA-SY-EN – 2017-05c – English
2.5.1
Measuring reference system
All actuator functions are based upon a uniform dimensional reference system. The algebraic signs of
all parameters set up are defined ex-factory as follows, viewing the input end of the motor:
–
Positive (+) = direction of movement with clockwise direction of rotation of motor shaft.
–
Negative (–) = direction of movement with anti-clockwise direction of rotation of motor shaft.
The direction of movement of load is e.g. dependent on the spindle type of the axis (clockwise/anti-
clockwise) and on the gear unit employed. When using angle or toothed belt gear units, the reverse
arrangement of direction of rotation may be of benefit
è
FCT [...][Application Data]Environment]:
Inverse Rotation Polarity..
Recommendation: check direction of movement in job mode and, if required, reverse it:
–
increasing actual values = positive direction (+)
–
decreasing actual values = negative direction (-)
Example: linear drive
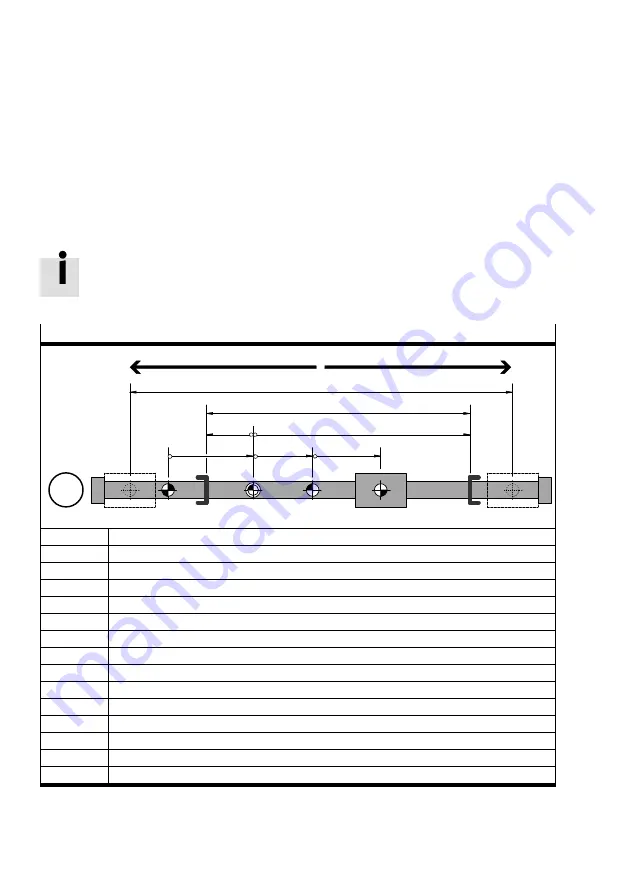
Ref
AZ
A
b
c
PZ
d
e
TP/AP
SLP
SLN
(+)
(–)
M
1
2
3
Ref
Homing point (reference point)
AZ
Axis zero point
PZ
Project zero point
SLN
Negative software end position (SW limit negative)
SLP
Positive software end position (SW limit positive)
SP
Target position
AP
Actual position
a
Offset axis zero point (AZ)
b
Offset project zero point (PZ)
c
Target/actual position (TP/AP)
d
Software limit negative (SLN)
e
Software limit positive (SLP)
1
Usable range (usage stroke)
2
Operating range (effective stroke)
3
Direction of movement with the factory setting
Tab. 2.21
Dimensional reference system
è
FCT [...][Axis][Measurements]
















































