Oxymitter 5000
E-10
Instruction Manual
IM-106-350, Rev 2.2
July 2008
STATUS HANDLING
If the input status on the PID block is Bad, the mode of the block reverts to
Manual. In addition, you can select the Target to Manual if Bad IN status
option to direct the target mode to revert to manual. You can set the status
option in Manual or Out of Service mode only.
NOTE
Target to Manual if Bad IN is the only status option supported by the PID
function block. Unsupported options are not grayed out; they appear on the
screen in the same manner as supported options.
APPLICATION
INFORMATION
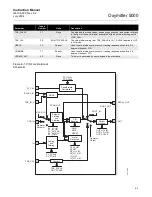
The PID function block is a powerful, flexible control algorithm that is
designed to work in a variety of control strategies. The PID block is configured
differently for different applications. The following examples describe the use
of the PID block for closed-loop control (basic PID loop), feedforward control,
cascade control with master and slave, and complex cascade control with
override.
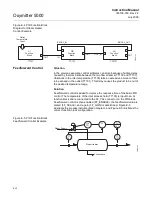
Closed Loop Control
To implement basic closed loop control, compute the error difference between
the process variable (PV) and setpoint (SP) values and calculate a control
output signal using a PID (Proportional Integral Derivative) function block.
The proportional control function responds immediately and directly to a
change in the PV or SP. The proportional term GAIN applies a change in the
loop output based on the current magnitude of the error multiplied by a gain
value.
The integral control function reduces the process error by moving the output
in the appropriate direction. The integral term RESET applies a correction
based on the magnitude and duration of the error. Set the RESET parameter
to zero for integral only control. To reduce reset action, configure the RESET
parameter to be a large value.
The derivative term RATE applies a correction based on the anticipated
change in error. Derivative control is typically used in temperature control
where large measurement lags exist.
The MODE parameter is a switch that indicates the target and actual mode of
operation. Mode selection has a large impact on the operation of the PID
block:
• Manual mode allows the operator to set the value of the loop output
signal directly.
• Automatic mode allows the operator to select a setpoint for automatic
correction of error using the GAIN, RESET, and RATE tuning values.
• Cascade and Remote Cascade modes use a setpoint from another
block in a cascaded configuration.
• Remote Out mode is similar to Manual mode except that the block
output is supplied by an external program rather than by the operator.
• Initialization Manual is a non-target mode used with cascade
configurations while transitioning from manual operation to automatic
operation.
Summary of Contents for Oxymitter 5000
Page 2: ......
Page 6: ......
Page 12: ......
Page 22: ...Oxymitter 5000 xii Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 42: ...Oxymitter 5000 1 20 Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 62: ...Oxymitter 5000 2 20 Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 74: ...Oxymitter 5000 4 6 Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 78: ...Oxymitter 5000 5 4 Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 94: ...Oxymitter 5000 7 6 Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 140: ...Oxymitter 5000 9 22 Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 184: ...Oxymitter 5000 B 2 Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 204: ...Oxymitter 5000 D 14 Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 222: ...Oxymitter 5000 E 18 Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 ...
Page 224: ...Instruction Manual IM 106 350 Rev 2 2 July 2008 Index 2 Oxymitter 5000 ...