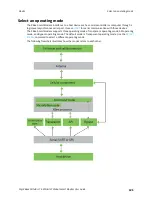
Cellular connection process
Connecting
Digi XBee3 Cellular LTE-M/NB-IoT Global Smart Modem User Guide
118
Connecting
In normal operations, the XBee Smart Modem automatically attempts both a cellular network
connection and a data network connection on power-up. The sequence of these connections is as
follows:
Cellular network
1. The device powers on.
2. It looks for cellular towers.
3. It chooses a candidate tower with the strongest signal.
4. It negotiates a connection.
5. It completes cellular registration.
Data network connection
1. The network enables the evolved packet system (EPS) bearer with an access point name
(APN). See
if you have APN issues.
2. The device negotiates a data connection with the access point.
3. The device receives its IP configuration and address.
4. The
command now returns a
0
and the sockets become available.
Data communication with remote servers (TCP/UDP)
Once the data network connection is established, communication with remote servers can be
initiated in several ways.
Note
For NB-IoT, TCP support is dependent on the network. Contact your network provider for
details.
n
Transparent mode data sent to the serial port (see
and
for timing).
n
API mode:
Transmit (TX) Request: IPv4 - 0x20
received over the serial connection.
n
Digi Remote Manager connectivity begins.
Data communication begins when:
1. A socket opens to the remote server.
2. Data is sent.
Data connectivity ends when:
1. The server closes the connection.
2. The
TM
timeout expires (see
TM (IP Client Connection Timeout)
).
3. The cellular network may also close the connection after a timeout set by the network
operator.