110
•
Additional Reference Information
Linea SWIR GigE Series Camera
Lens Modeling
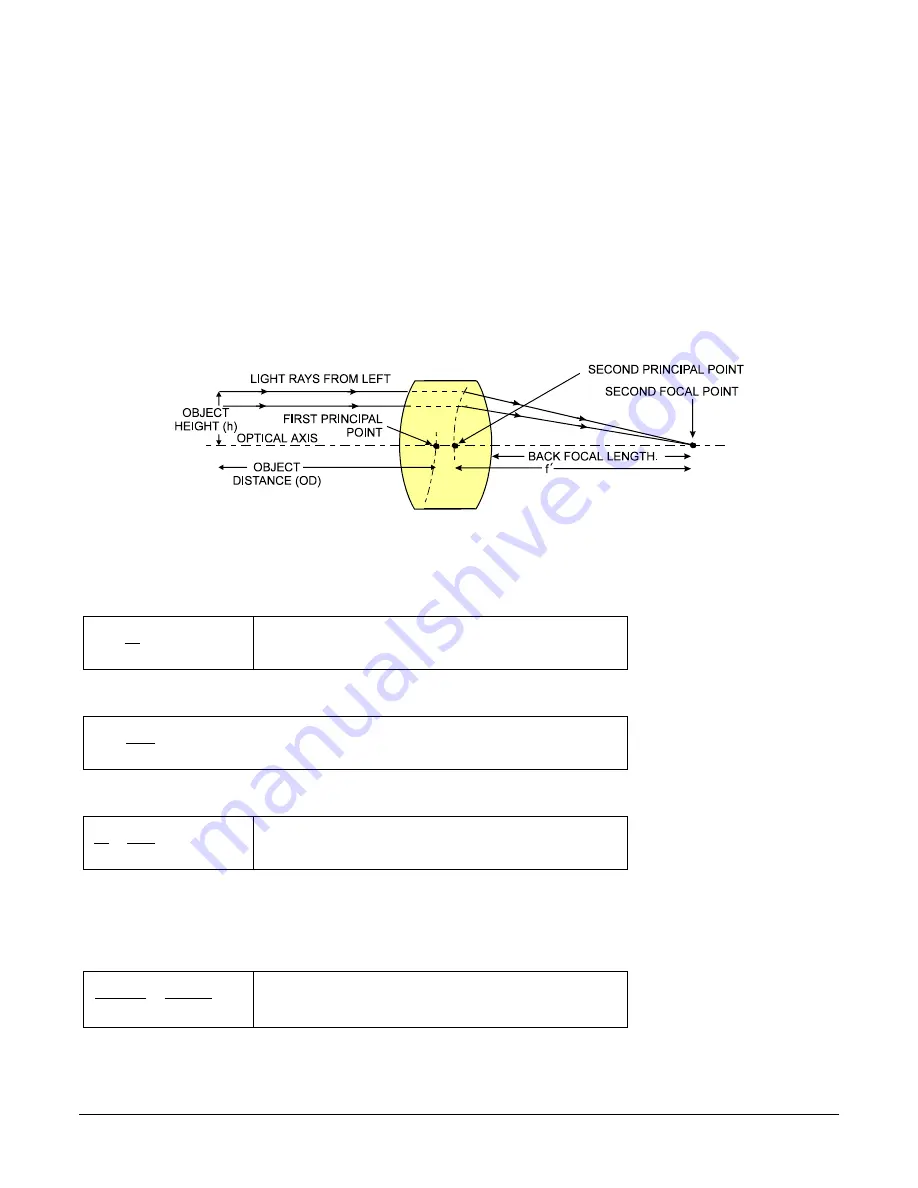
A lens surrounded by air may be modeled for camera purposes using three primary points: first
and second principal points and the second focal point. The primary points for a lens should be
available from the data sheet or manufacturer. Primed quantities denote characteristics of the
image side of the lens, h is the object height and h
′
is the image height.
The focal point is the point at which the image of an infinitely distant object is brought to focus.
The effective focal length (f
′
) is the distance from the second principal point to the second focal
point. The back focal length (BFL) is the distance from the image side of the lens surface to the
second focal point. The object distance (OD) is the distance from the first principal point to the
object.
Primary Points in a Lens System
Figure 67: Lens System Diagram
Magnification and Resolution
The magnification of a lens is the ratio of the image size to the object size:
h
h
m
'
=
Where m is the magnification, h’ is the image height (pixel
size) and h is the object height (desired object resolution
size).
By similar triangles, the magnification is alternatively given by:
OD
f
m
'
=
These equations can be combined to give their most useful form:
OD
f
h
h
'
'
=
This is the governing equation for many object and image
plane parameters.
Example:
An acquisition system has a 512 x 512-element 10 um pixel pitch, a lens with an effective
focal length of 45 mm and requires that 100
m
m in the object space correspond to each pixel in the
image sensor. Using the preceding equation, the object distance must be 450 mm (0.450m).
OD
mm
m
m
45
100
10
=
m
m
)
450
.
0
(
450
m
mm
OD
=
















































