9
If current through the temperature sensor exceeds the values
listed, an intermediate control circuit relay must be used
to reduce the current or the sensor will not work properly.
TEMPERATURE SENSOR ELECTRICAL RATINGS
Volts
Continuous
Amperes
Inrush
Amperes
110-120
3.00
30.0
220-240
1.50
15.0
440-480
0.75
7.5
600
0.60
6.0
C-4.2-2) Single Phase (Standard) -
The type of in-winding
overload protector used is referred to as an inherent overheating
protector and operates on the combined effect of temperature
and current. This means that the overload protector will trip
out and shut the pump off if the windings become too hot, or
the load current passing through them becomes too high. It
will then automatically reset and start the pump up after the
motor cools to a safe temperature. In the event of an overload,
the source of this condition should be determined and rectified
immediately.
DO NOT LET THE PUMP CYCLE OR RUN IF
AN OVERLOAD CONDITION OCCURS !
C-4.3) Moisture Sensors- DS Models: (Optional)
A normally open (N/O) detector is installed in the pump
seal chamber which will detect any moisture present. It is
recommended that this detector be connected in series to an
alarm device or the motor started coil to alert the operator that a
moisture detect has occurred. In the event of a moisture detect,
check the individual moisture sensor probe leads for continuity,
(∞ resistance = no moisture) and the junction box/control box
for moisture content. The above situations may induce a false
signal in the moisture detecting circuit. If none of the above
tests prove conclusive, the pump(s) should be pulled and the
source of the failure identified and repaired.
IF A MOISTURE
DETECT HAS OCCURRED SCHEDULE MAINTENANCE AS
SOON AS POSSIBLE.
C-4.4) Wire Size:
Consult a qualified electrician for proper wire size if additional
power cord length is required. See table on pages 9 and 10
for electrical information.
SECTION: D START-UP OPERATION
D-1) Check Voltage and Phase:
Before operating pump, compare the voltage and phase
information stamped on the pump identification plate to the
available power.
D-2) Check Pump Rotation:
Before putting pump into service for the first time, the motor
rotation must be checked. Improper motor rotation can
result in poor pump performance and can damage the motor
and/or pump. To check the rotation, suspend the pump
freely, momentarily apply power and observe the “kickback”.
“Kickback” should always be in a counter-clockwise direction
as viewed from the top of the pump motor housing.
D-2.1) Incorrect Rotation for Three-Phase Pumps:
In the event that the rotation is incorrect for a three-phase
installation, interchange any two power cord leads at the
control box.
DO NOT
change leads in the cord housing in the
motor. Recheck the “kickback” rotation again by momentarily
applying power.
D-2.2) Incorrect Rotation for Single-Phase Pumps:
In the unlikely event that the rotation is incorrect for a single
phase pump, contact a Barnes Pumps Service Center.
D-3) Identification Plate:
Record future serial plate information in the “NOTES” section.
D-3.1) Pump-Down Test:
After the pump has been properly wired and lowered into the
basin, sump or lift station, it is advisable to check the system
by filling with liquid and allowing the pump to operate through
its pumping cycle. The time needed to empty the system, or
pump-down time along with the volume of water, should be
recorded on the start-up report.
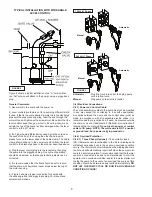
SECTION E: PREVENTATIVE MAINTENANCE
As the motor is oil filled, no lubrication or other maintenance
is required, and generally Barnes Pumps will give very reliable
service and can be expected to operate for years on normal
sewage pumping without failing. In our experience attempts
at preventative maintenance are more likely to reduce, rather
than extend the life of our pumps. However, if you are inclined
to perform preventative maintenance, the following are the
steps that should be performed.
1) Inspect motor chamber for oil level and contamination
and repair as required per section F-1.
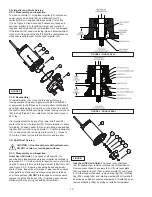
2) Inspect impeller and body for excessive build-up or
clogging and repair as required per section F-2.
3) Inspect motor and bearings and replace as required
per section F-3.
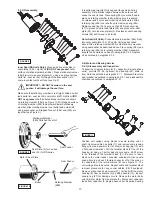
4) Inspect seal for wear or leakage and repair as required
per section F-4.
Summary of Contents for 104872
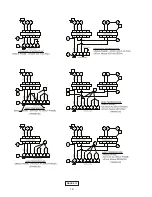
Page 16: ...16 FIGURE 13 ...
Page 17: ...17 FIGURE 13 ...
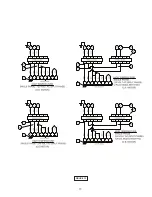
Page 18: ...18 FIGURE 13 CONTIUED ...
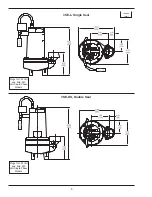
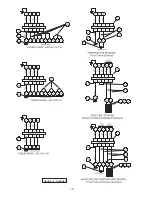
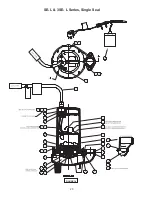
Page 20: ...20 FIGURE 16 SE L 3SE L Series Single Seal ...
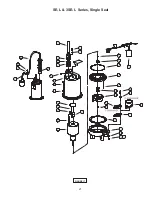
Page 21: ...21 FIGURE 17 SE L 3SE L Series Single Seal ...
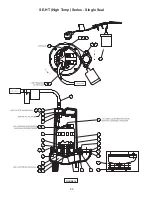
Page 22: ...22 FIGURE 18 SE HT High Temp Series Single Seal ...
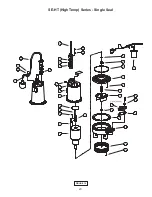
Page 23: ...23 FIGURE 19 SE HT High Temp Series Single Seal ...
Page 24: ...24 FIGURE 20 3SE DS Series Double Seal ...
Page 25: ...25 FIGURE 21 3SE DS Series Double Seal ...
Page 29: ...29 Notes ...
Page 30: ...30 Notes ...