OM_CLS_-_EN_2-0
47
CLS
Advance
Troubleshooting
10.2
Status & error messages
The CLS transmits detailed status and error messages to the control software.
The messages report on events of interest that happen while the CLS is operating. Errors can be
generated by every intelligent CLS unit such as the coin validator or the hoppers also attempting
to resolve their own errors. If they cannot clear the errors, the CLS will pass the relevant error
code to the control software.
Usually, the error codes are translated to explicit error messages in the control software describing
the error location and tips on how to correct the errors. In this case you will not need the tables below.
If not, the Troubleshooting Tables below list the error category depending on the gravity of the
error concerning the CLS operation as well as related information also useful in helping how to
handle the error.
10.2.1
Error categories
The CLS will attempt to resolve any errors or problem situations without external intervention.
Events are prioritized in the categories defined below:
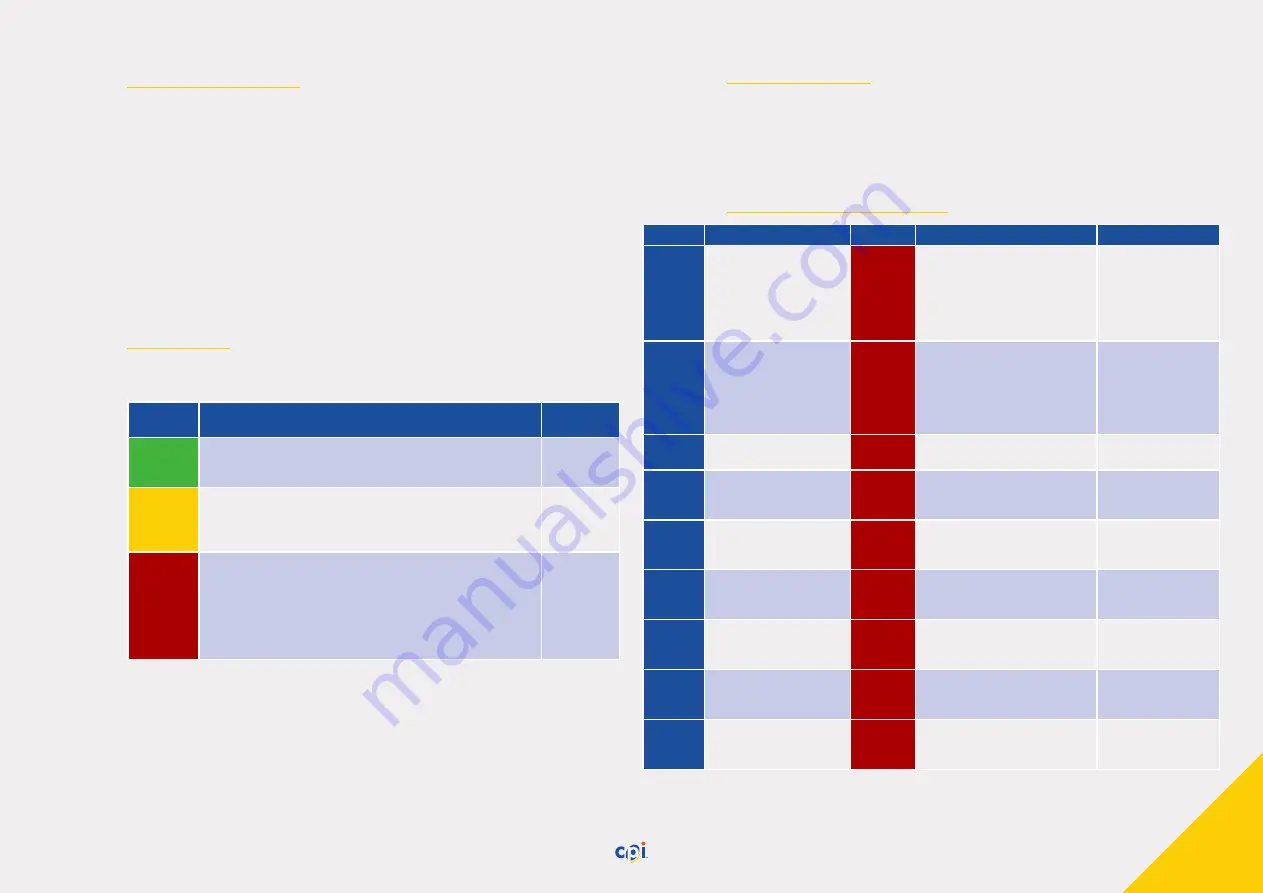
Category Description
Who can
help?
Informa-
tional
The event will be recorded and transmitted to the control software
but the CLS will continue to operate correctly and no intervention is
required.
–
Attention
This error will require intervention by the operator and indicates the CLS
is currently not operating or shortly will not be capable of correct opera-
tion without intervention by the attendant/service. Examples might be a
coin jam, a hopper running out of coins
Attendant/
Service
Critical
This error indicates that it is likely that some component in the CLS has
failed and needs to be replaced. The error is severe enough to cause the
machine to stop operating and intervention by the attendant will likely
be insufficient to repair the problem, although the control software can
recommend a course of action involving the attendant. One example
might be an output failure on the CLS main PCB or a communication
failure between the CLS units.
Attendant/
Service
10.2.2
Troubleshooting tables
The following tables list the error codes transmitted by the
• CLS control unit
• CLS coin validator
• CLS coin hoppers
10.2.2.1
Error codes transmitted by the CLS control unit
Error code Description/Cause
Category
Remedy/hints
By whom
0x0001
Hopper count mismatch after
system start-up. Number of
hoppers identified are not
matching with the number
configured in the system
Critical
• Make sure that all hoppers are
installed and engaged correctly
(cf. Chap. "7.5 Removing and reinstall-
ing a coin hopper", p. 30)
• Configuration failure, contact
service
• Attendant possess-
ing the key for the
lower lock
• Service
0x0002
Hopper denomination
mismatch after system
start-up. Hopper denomina-
tions and country code are
not matching with the payout
configuration
Critical
Configuration failure, contact service
Service
0x0010
Main controller RAM fault. Its
memory is defect
Critical
Hardware replacement, contact
service
Service
0x0012
Main controller warning. Its
stack-based memory has
run out
Critical
Programming failure, contact Service Service
0x0013
Main controller warning.
Its non-volatile memory is
defect
Critical
Hardware replacement, contact
service
Service
0x0014
Main controller warning.
Real-time clock battery for
backup missing
Critical
Initialization, Hardware replacement,
contact service
Service
0x0020
Main controller warning.
Its internal CX2 queue has
run out
Critical
Programming failure, contact Service Service
0x0021
Main controller warning. Its
internal hopper queue has
run out
Critical
Programming failure, contact Service Service
0x0022
Main controller warning.
Its internal control request
queue has run out
Critical
Programming failure, contact Service Service






























