HP solution: high-efficiency three-phase UPSs
The HP R8000, R12000, and RP12000/3 (the latter
shown in Figure 5) are three-phase UPSs that use a
hybrid design combining the best features of single-
conversion and double-conversion topologies. This
double conversion-on-demand (DCOD) topology
(Figure 6) offers the efficiency of a single-conversion
UPS with the performance of a double-conversion
system. Power from the AC mains that meets preset
conditions bypasses most of the processing circuitry
and is applied to the output for routing to the power
distribution panels. During periods when the AC input
is irregular or out of tolerance, the rectifier and inverter are switched to DCOD operation to process
the AC input and provide a three-phase AC output that meets load requirements. When AC input
power is absent, the system goes into battery mode.
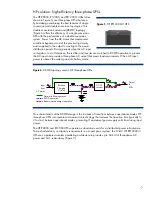
Figure 5
. HP RP12000/3 UPS
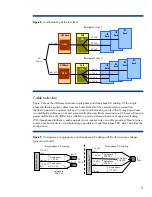
Figure 6
. DCOD topology used in HP three-phase UPSs
One characteristic of the DCOD design is the increase of transitions between operational modes. HP
three-phase UPSs incorporate minimum-switch technology that reduces the transition time (typically to
2 to 4 ms) between operational modes, preventing IT equipment power supply units from losing input
power.
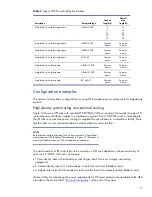
The HP R8000 and R12000 UPSs operate as stand-alone units for a distributed power infrastructure.
To meet redundancy or capacity requirements in a zoned power system, the 12-kW HP RP12000/3
UPS uses a patented wireless paralleling architecture to provide up to 60 kW of three-phase AC
power and N+1 redundancy (Figure 7).
Input
from
AC mains
Output
to
PDPs
Normal (offline) operation
DCOD operation
Battery (stored energy) operation
DC-AC
Inverter
Rectifier/
Charging
Circuitry
7