InteliPro, SW version 1.4,
©
ComAp
–
April 2014
InteliPro 1.4 Comprehensive Guide - rev. 1
2-17
island mode, the generators, running in parallel with the islanded area, would start to supply its
complete consumption, generating current in opposite direction. DOC protection is used to avoid this
situation, and trip the generator from the islanded mains, combining the overcurrent protection
together with its directional character. Compared to the "reverse power protection", DOC protection
detects also reactive currents from the given angle zone, what allows better sensitivity for tripping.
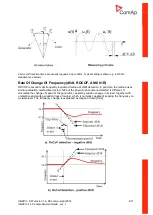
The following image shows the conditions of activation of Directional Overcurrent protection in
InteliPro
–
i.e. critical angles between voltage and current, given the voltage is placed at the 0°angle:
The setting is done using the setpoints in the group
. The unit allows top test the functionality of
the directional overcurrent protection by setting the setpoint
output
DOC Test
shows the sensing of the protection regardless of the other protection
enabling/disabling conditions in order to allow full quadrant range test of this protection stage.
Neutral Voltage Displacement (NVD, ANSI 59N)
NVD protective function is used in medium or high voltage systems with isolated or indirectly grounded
zero-point. Under healthy conditions of the system, the sum of the three phase-to-earth voltages
should balance to zero. When an earth-fault occurs, it does not cause a short-circuit, because of the
isolation of the system in the zero point. However, the fault provides connection of one phase with
earth what represents hazard for the system safety (ground-fault in any other phase would then mean
a phase-to phase short-circuit, phase-to-ground voltage of the other phases may fluctuate to multiples
of its nominal, providing increased stress to the isolation system, etc). One of the effects of the fault is
a rise in the neutral voltage, so called neutral voltage displacement. This neutral voltage displacement
is measured in a specific "open-delta" connection of voltage transformers, as shown in the chapter
. In some cases, it is required to clear the fault by tripping the appropriate
circuit breaker. However, the NVD protection itself does not allow detecting the location of a fault and
for this reason it is sometimes used only for providing an earth-fault alarm.
0°
90°
-
90°
DOC>
Trip area
150°
-
60°
Base angle
-
135°