Chapter 3
Installation and Configuration
3-6 CallConnector Operator
Router Configuration for CallConnector Operator
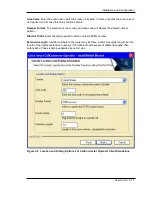
The CallConnector Operator installation requires certain configuration on the CME Router. These
include:
Configure the Operator’s IP Phone(s)
: The CallConnector Operator application allows the
operators to control the calls on their IP phone from the PC. This requires the phone to be
configured with directory numbers and features suitable for the operator call handling functions.
Call Routing to the Operator Phones
: There can be several categories of calls received by the
operators each requiring a distinct call treatment. Examples of such call categories might include
the Main Number calls, Customer Support calls, Sales calls or Internal calls. The routing of these
calls to the operator phones needs to be configured in the Cisco Router. Generally these calls will
be directed to different numbers in the attendant’s phone.
Multiple Operators Deployments
: If the organization has multiple operators, the calls need to
be distributed to the operators. The recommended method is to use a hunt group for each
operator call queue. See below for more details.
Busy and Night Service Routing
: When the operators are not available during the work day the
incoming calls need to be routed either to an alternate number or to voice mail. For off-hour call
routing, the Cisco router night service routing can be enabled.
Park and Page Numbers
: Park slots or directory numbers need to be configured on the router to
allow the operators to park the calls and make overhead announcements.
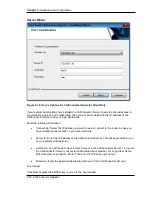
Configuration of the Operator’s Phone
The attendant’s IP phone is required to be a multi-line Cisco IP Phone with sufficient capacity to
handle the operator calls. The considerations for configuring the attendant’s phone include:
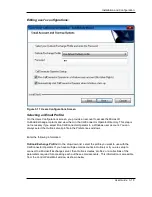
Number of Call Queues:
An operator can be configured with multiple call queues. Each call queue is comprised of one or
more directory numbers on the operator phone. The number of directory numbers required
depends on the maximum number of calls that are expected concurrently at that attendant’s
phone and the number of channels for directory numbers. We recommend that the attendant’s
directory numbers be configured to have eight channels i.e. are octal-line DNs.
As an example, let us configure an operator with three incoming call queues – Main Number,
Sales and Support. The Main Number queue could have up to six call waiting, which the sales
and support generally do not exceed for concurrent calls.
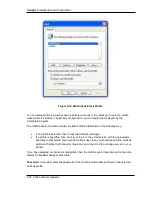
Number and type of Directory Numbers or DNs:
For the three queues above, we can use four octal-line DNs to receive all the operator calls. Two
DNs, with a total of sixteen channels, for the Main Number queue. One DN each with eight
channels for Sales and Support calls.
In addition, the operator phone should have a personal DN for receiving and making their own
calls.