10-13
Cisco ASA Series Firewall CLI Configuration Guide
Chapter 10 NAT Examples and Reference
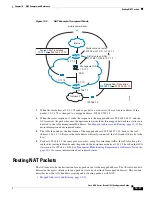
Routing NAT Packets
The Same Address as the Real Address (Identity NAT)
The default behavior for identity NAT has proxy ARP enabled, matching other static NAT rules. You can
disable proxy ARP if desired. You can also disable proxy ARP for regular static NAT if desired, in which
case you need to be sure to have proper routes on the upstream router.
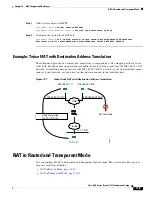
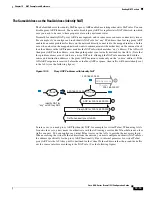
Normally for identity NAT, proxy ARP is not required, and in some cases can cause connectivity issues.
For example, if you configure a broad identity NAT rule for “any” IP address, then leaving proxy ARP
enabled can cause problems for hosts on the network directly connected to the mapped interface. In this
case, when a host on the mapped network wants to communicate with another host on the same network,
then the address in the ARP request matches the NAT rule (which matches “any” address). The ASA will
then proxy ARP for the address, even though the packet is not actually destined for the ASA. (Note that
this problem occurs even if you have a twice NAT rule; although the NAT rule must match both the
source and destination addresses, the proxy ARP decision is made only on the “source” address). If the
ASA ARP response is received before the actual host ARP response, then traffic will be mistakenly sent
to the ASA (see the following figure).
Figure 10-10
Proxy ARP Problems with Identity NAT
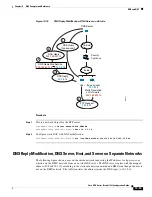
In rare cases, you need proxy ARP for identity NAT; for example for virtual Telnet. When using AAA
for network access, a host needs to authenticate with the ASA using a service like Telnet before any other
traffic can pass. You can configure a virtual Telnet server on the ASA to provide the necessary login.
When accessing the virtual Telnet address from the outside, you must configure an identity NAT rule for
the address specifically for the proxy ARP functionality. Due to internal processes for virtual Telnet,
proxy ARP lets the ASA keep traffic destined for the virtual Telnet address rather than send the traffic
out the source interface according to the NAT rule. (See the following figure).
209.165.200.225
209.165.200.230
209.165.200.231
Identity NAT for
“
a
ny” with Proxy ARP
O
u
t
s
ide
In
s
ide
1
2
4
ARP for 209.165.200.230.
Tr
a
ffic incorrectly
s
ent to A
S
A.
Proxy ARP for 209.165.200.230.
3
ARP Re
s
pon
s
e
Too l
a
te
Summary of Contents for ASA 5508-X
Page 11: ...P A R T 1 Access Control ...
Page 12: ......
Page 157: ...P A R T 2 Network Address Translation ...
Page 158: ......
Page 233: ...P A R T 3 Service Policies and Application Inspection ...
Page 234: ......
Page 379: ...P A R T 4 Connection Management and Threat Detection ...
Page 380: ......