56
Operation
Level Grouping
It is not possible to take different sources to the destination on the same level. For instance,
you cannot take SD from two different sources. The outcome would be noise even if you
could do it. (That is because routers are not mixers.)
Level Grouping
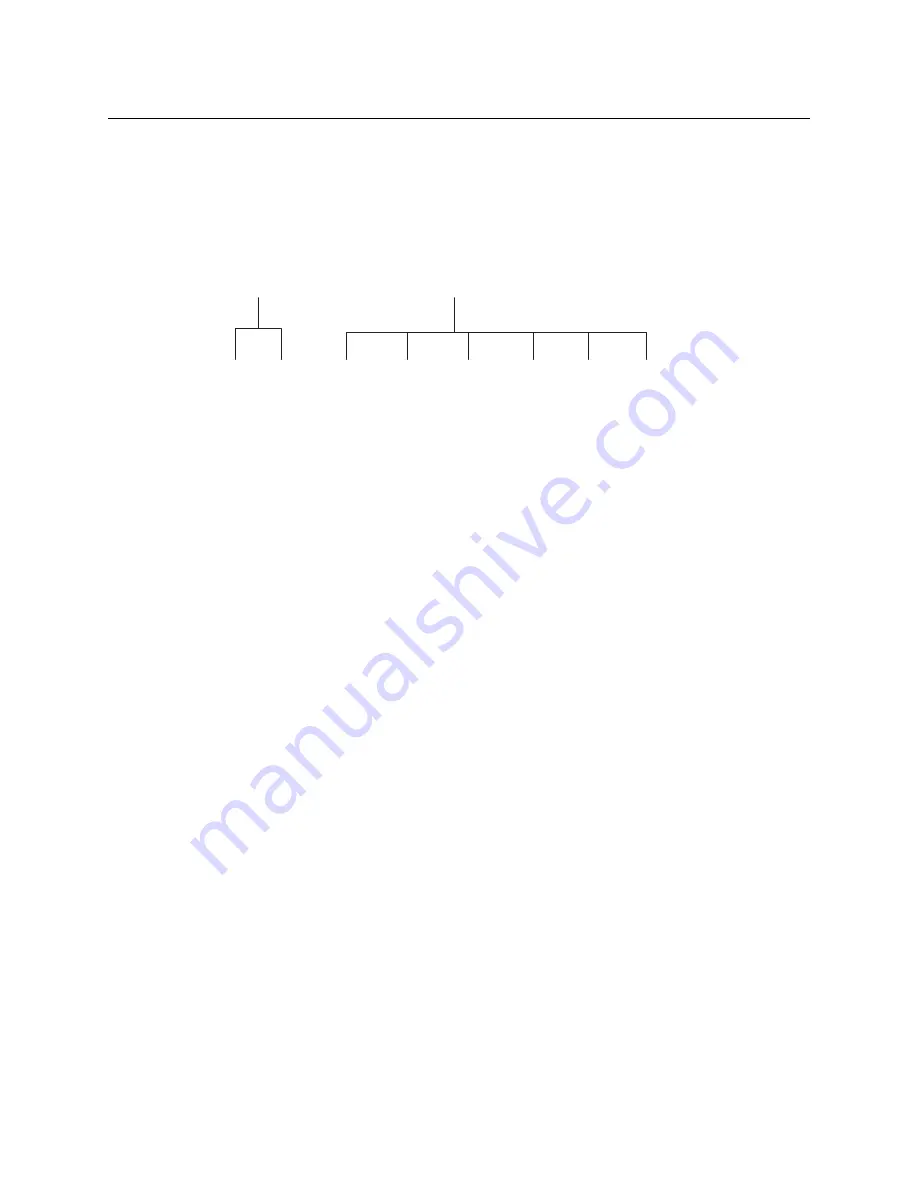
Virtual levels can be grouped. This diagram illustrates grouping:
There are two types of virtual levels: basic and abstract. Basic virtual levels are those that
correspond to actual physical levels. Abstract virtual levels do not correspond to physical
levels. In the illustration, the 5 “Aud
x
” levels are grouped under ‘Audio’. The two video levels
are grouped under ‘Video’.
The levels ‘Video’ and ‘Audio’ are abstract levels; the other levels are basic levels.
The NV9641, at present, ignores the concept of level groups, and presents any config-
ured level groups as completely expanded. That is, it always displays basic levels and
never abstract levels.
Hold
Hold mode (and hold buttons) apply in both X-Y mode and multi-destination mode.
Breakaway
In X-Y mode, a hold button retains breakaway levels after a take.
Simply press the hold button at any time before the take.
A hold button is a toggle. Press it once to put the panel in hold mode; press it again to
remove hold mode.
Multi-Destination Mode
In multi-destination mode, hold mode allows you to select more than one MD destination
at a time. The selections also remain selected after a take.
Category Selection
In the NV9000 system, devices are assigned to categories, where the devices within the
categories are either numbered or identified by alphanumeric suffixes. For instance, a
category representing cameras might be CAM and the cameras in the category might be
named CAM1, CAM2, and so on.
NV9641 category buttons can represent either a source category or a destination category
(but not both). When you pressing category buttons to begin device selection, one of two
things occurs:
HD
SD
Aud1
Aud2
Aud3
Aud4
Aud5
Video
Audio
. . .






























