Product overview
2.7
Integration into TwinCAT
The brake module can be integrated in the TwinCAT
System Manager as a completely normal I/O device
(1) and is parameterized (3) with the TCDrive
Manager (2).
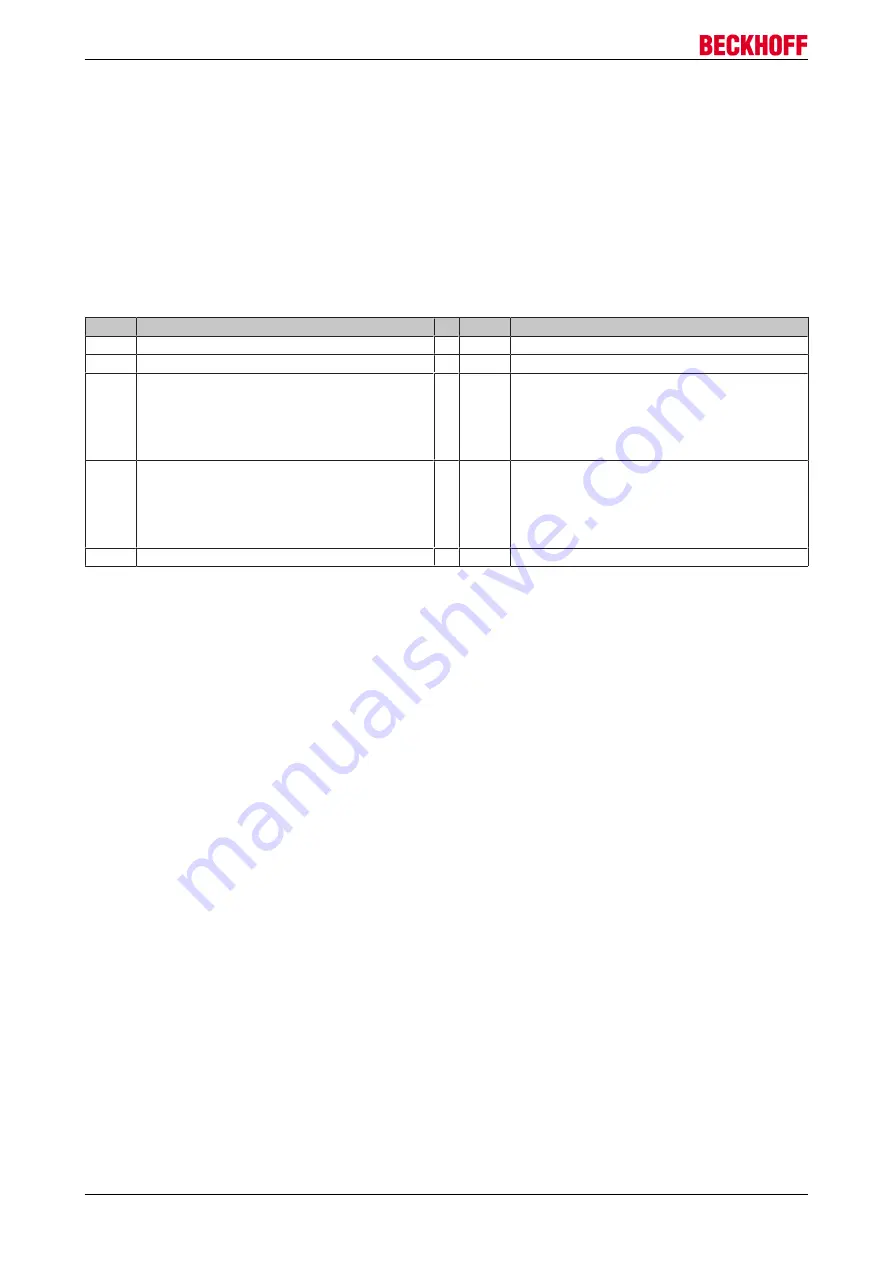
Power Management
Configuration in the TC Drive Manager
Pos.
Name
Pos.
Name
1
Power management
6
Activation / deactivation of the internal brake resistor
2
Mains voltage selection
7
External brake resistor parameter list
3
Phase monitoring (deactivate for single-phase mains)
8
0 = Deactivation of the external brake resistor
(
not
recommended)
1 = Standard energy management with external
brake resistor
2 = Energy management with external
brake resistor (standalone)
4
Delay time until the phase monitoring responds (acti-
vate if mains is unclean)
9
Enabling / disabling the fan of the external brake resis-
tor and setting the switching thresholds Switch on
Level: Percentage specification of the rated capacity
value of the external brake resistor.Switch on Temp.:
Max. temperature value for the external brake resistor
in "°C".
5
Internal brake resistor parameter list
2.8
Energy management
Intelligent energy management ensures that energy is distributed evenly to the DC links and the internal
brake resistors when devices are used commonly in the drive system. This reliably prevents the undesirable
permanent load of only one device.
2.8.1
DC link
The connected servomotors are supplied with energy from the DC link. It serves as an energy storage and
first needs to be charged up after switching the device on, before it can supply the servomotors. The DC link
is designed such that it can take up and store a certain degree of surplus energy from the motor (brake
energy) and subsequently supply the motor again with this stored energy. If the upper limit of the energy
storage is reached, the brake chopper feeds any further brake energy into the internal or external brake
resistor, where it is converted into heat; it is then no longer available for the further operation of the motor.
The voltage is taken and evaluated as the indicator for the current energy level of the DC link. As soon as
the brake resistors have also reached their energy limit, the error ‘FD4C, DC link – overvoltage’ appears and
the energy flow to and from the motor is interrupted, i.e. the motor makes uncontrolled movements.
In a drive system, the DC links of the individual devices are connected so that the energy level of all devices
is the same, regardless of which motor the brake energy is currently being fed back from. In many cases
these feedbacks do not happen at the same time, and
without
a DC link system, for example, a device
would be at the limit and would already have to "destroy" energy in a brake resistor, even though other
devices could still store energy in the DC link. In a DC link connection the energy could be stored, since the
DC link of all linked devices would be loaded first, before the energy in the brake resistors would be
converted to heat.
AX5000 Brake module AX5021
8
Version: 1.3
Summary of Contents for AX5021
Page 2: ......




























