AWS Storage Gateway User Guide
Creating a Gateway Using a VPC Endpoint
2. Use the CLI to activate the gateway by specifying the activation key you received in previous step.
For example:
aws --region us-east-1 storagegateway activate-gateway --activation-key
BME11-LQPTD-DF11P-BLLQ0-111V1 --gateway-type FILE_S3 --gateway-name user-
ec2-iad-pl-fgw2 --gateway-timezone GMT-4:00 --gateway-region us-east-1
Example response:
{"GatewayARN": "arn:aws:storagegateway:us-east-1:123456789012:gateway/sgw-FFF12345"}
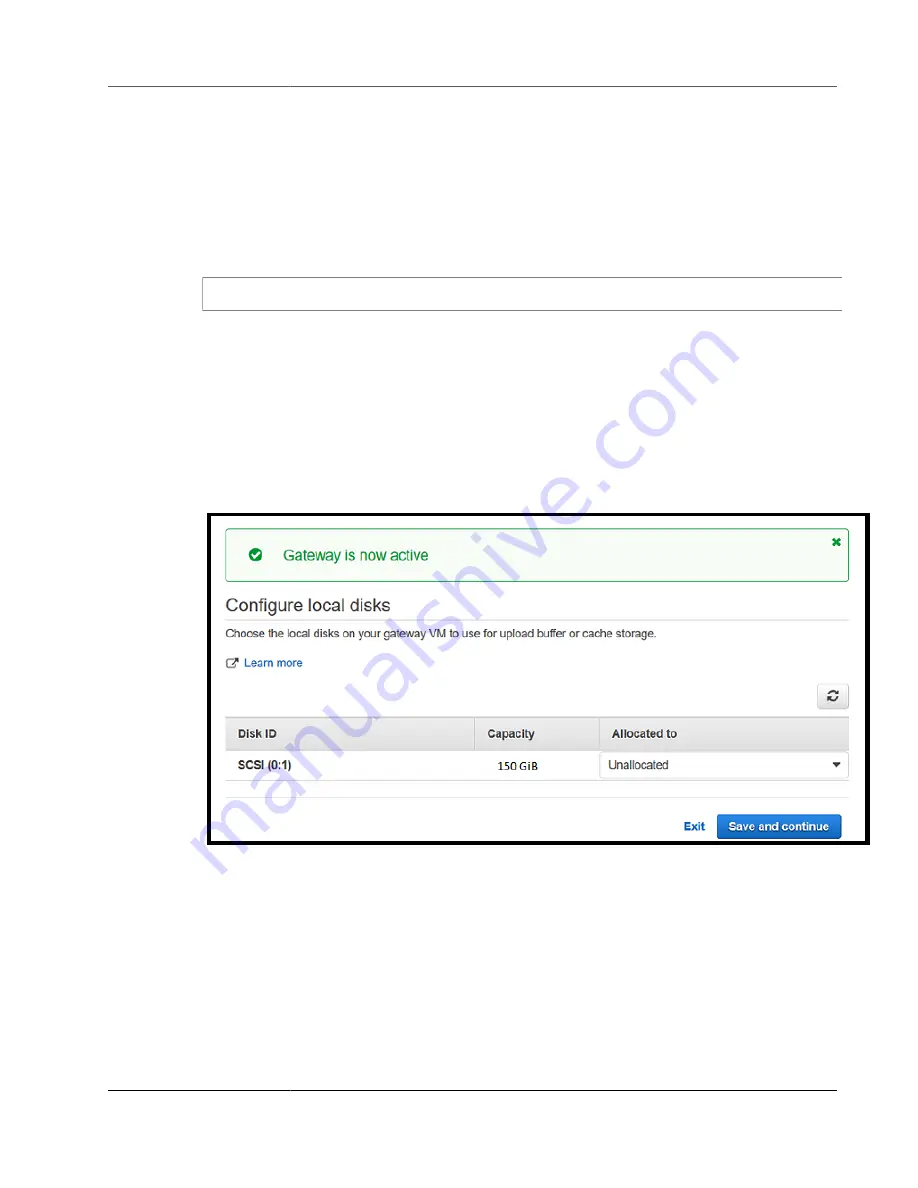
Configure Local Disks
When you deployed the VM, you allocated local disks for your gateway. Now you configure your gateway
to use these disks.
To configure local disks
1. On the
Configure local disks
page, identify the disks you added and decide which ones you want
to allocate for cached storage. For information about disk size limits, see
Sizes For Your Gateway (p. 397)
.
2. Choose
Cache
for the disk you want to configure as cache storage.
If you don't see your disks, choose
Refresh
.
3. Choose
Save and continue
to save your configuration settings.
Allow Traffic to Required Ports in Your HTTP Proxy
If you are using a HTTP Proxy, you need to allow traffic from Storage Gateway to the destinations and
ports listed below.
When Storage Gateway is communicating through the public endpoints, it communicates with the
following Storage Gateway services.
API Version 2013-06-30
142






























