Basic Guidelines
A graphic equalizer adjusts the sound of your audio system. Before setting the sliders, listen to your system and ask
yourself what you'd like to change about its sound. If you want more bass, for example, either raise the low frequency
sliders or lower the midrange or high frequency sliders. Do this for both channels. Conversely, if you'd like to hear
more high frequencies, either raise the high frequency sliders or lower the midrange or bass frequencies.
Using The Controls
Power
Press this switch to turn the unit on or off. The red LED in the switch will light to show power is on.
Level
These knobs individually control the volume level of each channel.
Line
This switch refers to the hookups on the back of the EQ 25.1. If you are using XLR or balanced inputs (line 2),
depress this button. If you are using RCA or unbalanced inputs (line 1), leave this button in the out position.
EQ/Pass
Use this switch to compare the equalized and unequalized sound. Depress this button to hear the equalized sound.
Leave this switch in the out position to hear the unequalized sound.
EQ Sliders
There are five sliders each for Channels 1 and 2, which usually correspond to the left and right channels. Each slider
has a range of 12 dB to boost or cut its particular frequencies. The lowest frequency sliders (60 Hz) are on the left,
the highest frequencies (10 kHz) on the right. The range of this EQ corresponds with all but the extremes of human hearing. Adjusting the sliders makes
it simple to alter the sound of your system. For instance, the lowest note of a bass guitar is around 42 Hz. Adjusting the 60 Hz sliders adjusts the level of
the bass guitar, bass drum, and other instruments within this frequency range. Usually, identical adjustments should be made for each channel.
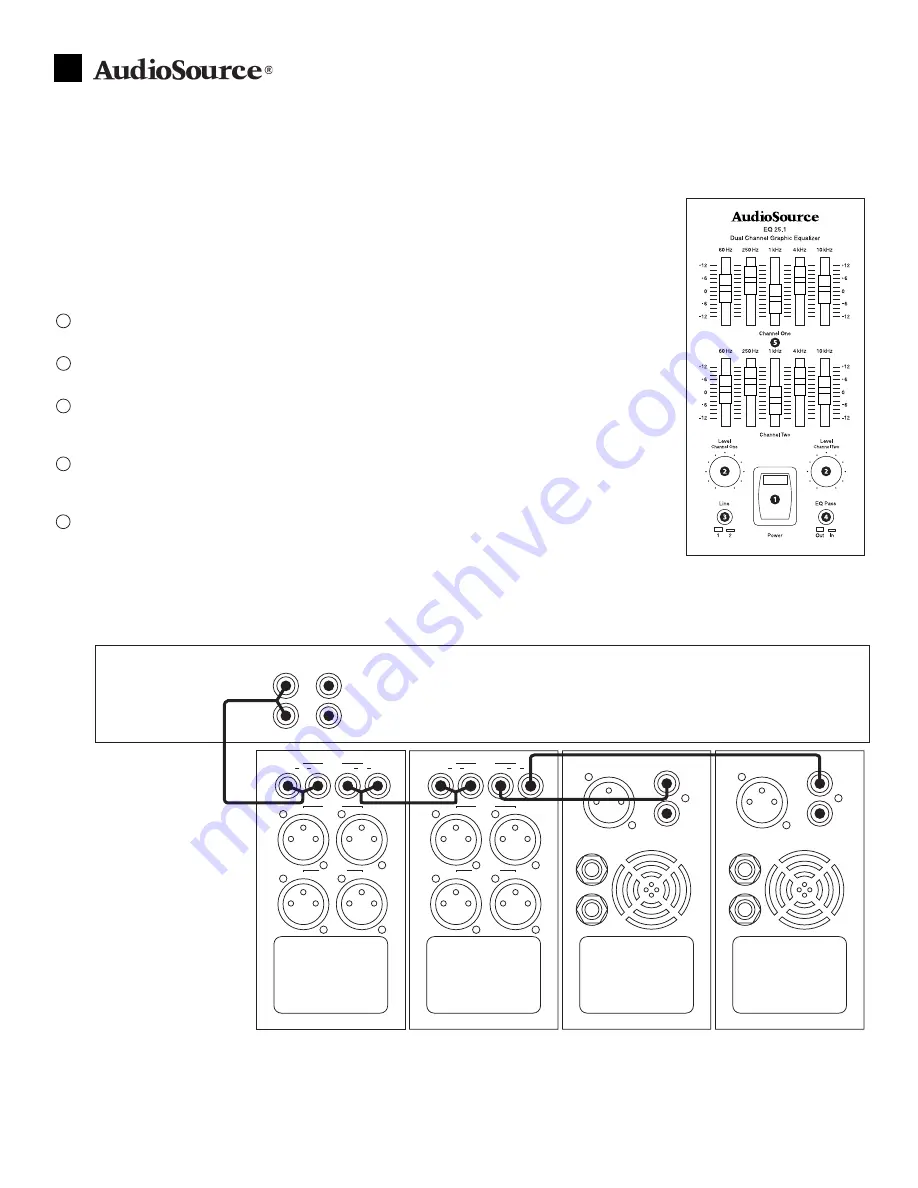
Hooking It Up
When connecting the EQ 25.1,
turn off or unplug your
components. This prevents
loud “pops” that might
damage your speakers
while you connect the cables.
We recommend that you use the
EQ 25.1 with a preamplifier or
other sort of mixer. The diagram
at right shows the EQ 25.1 in
conjunction with other compo-
nents from AudioSource’s modular
separates line. You can substitute
any amp or preamp; the setup
is the same. Also, XLR/balanced
connections follow the same paths
as the RCA/unbalanced connec-
tions described below.
1. Connect the source component (e.g. DVD player, CD player, cassette deck, microphone) to the preamp input.
2. Connect the two output channels of the preamp to the EQ inputs. In this diagram, Channel 1 is left and Channel 2 is right.
3. Connect the Channel 1 and 2 outputs from the EQ to the amplifier inputs. Please note that the Amp 5.1 is a single-channel monoblock amplifier, which
is why two of them are required in this example. Rather than two monoblocks, you could also use a single stereo amplifier, such as an Amp 6.2 or 6.3.
5
4
3
2
1
Owner’s Manual
EQ 25.1
Balanced Input
Speaker Output
+
–
Unbalanced
Line In
Line Out/
Thru
120 VAC 60 Hz 200 Watts
Amp 5.1
Balanced Input
Speaker Output
+
–
Unbalanced
Line In
Line Out/
Thru
120 VAC 60 Hz 200 Watts
Amp 5.1
Ch. 1 In
Ch. 2 In
Ch. 1 Out
Line 2
Line 2
Ch. 2 Out
120 VAC 60 Hz 12 Watts
In
Ch. 1
Ch. 2
Out
Ch. 1
Ch. 2
Line 1
Preamp 5.1
DVD Player,
CD Player or
Other Source
L
Audio Out
R
L
Audio In
R
Ch. 1 In
Line 2
Ch. 2 In
Ch. 1 Out
Line 2
Ch. 2 Out
120 VAC 60 Hz 12 Watts
In
Ch. 1
Ch. 2
Out
Ch. 1
Ch. 2
Line 1
EQ 25.1
Modular Dual Channel Graphic Equalizer
EQ 25.1
Note: If any part of this product is damaged or missing, do not contact your AudioSource dealer. Please call us directly at 800-435-7115.


