Page 35
© 2001-2015 attocube systems AG. Product and company names listed are trademarks or trade names of their respective
companies. Any rights not expressly granted herein are reserved. ATTENTION: Specifications and technical data are subject
to change without notice.
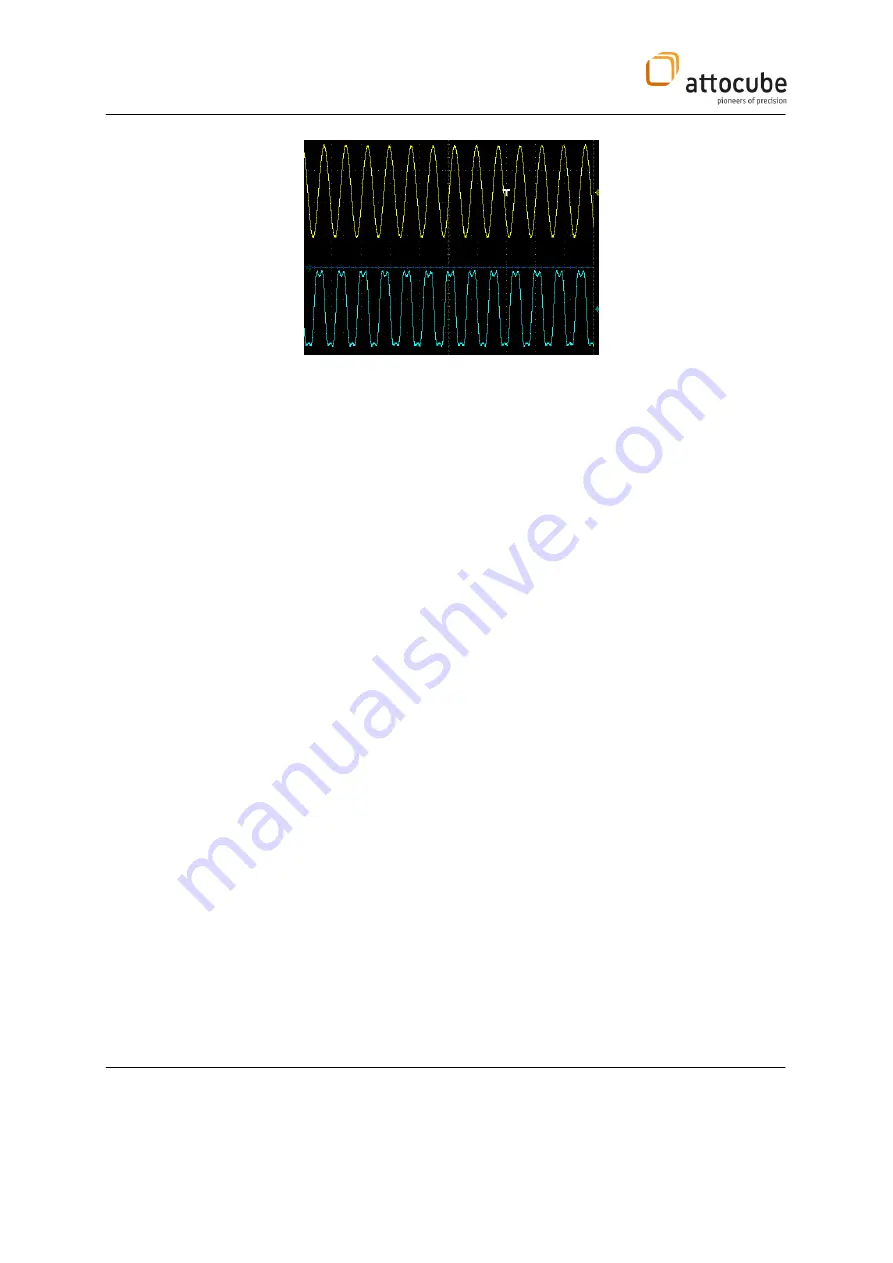
Figure 17
: Electrical signals corresponding to the dither excitation (top) and interference signal (bottom).
V.1.d.
MFM and EFM measurements
MFM (EFM) is performed in non-contact mode utilizing a magnetic
(conducting) tip, i.e. the tip of the cantilever is covered with hard-magnetic
or conductive material. The tip-sample interaction leads to a shift
f of the
lever mechanical resonance frequency f
0
. This interaction is directly related
to the gradient
F of the magnetic force acting on the tip along the lever
bending direction. For a given lever of spring constant K (>>
F), the
relation between the force gradient and the frequency shift
f (<< f
0
)
is
given by the approximation
F
-2 (
f/ f
0
) K.
Thus, the magnetic (electric) information can be either extracted from the
detected phase shift while measuring at a const. frequency or
correspondingly from the measured frequency shift in a phase-lock loop.
In order to avoid mixing of topographic and magnetic (electric)
information, the magnetic signal is usually recorded at bigger tip-sample
distances.
V.1.e.
KPFM measurements
KPFM is performed in non-contact mode utilizing a conductive tip, i.e. the
tip of the cantilever is covered with a contactable conductive material. In
contrast to the MFM or EFM modes the cantilever is not mechanically excited
at its resonance frequency by using the dither piezo but by using an
oscillating electrical tip AC potential. The oscillation amplitude thereby
depends on the tip to sample DC vol
t
age difference. Hence, by keeping the
oscillation amplitude at its minimum (i.e. HFx=0) with means of tuning the
















































