6.1.3 Modbus/TCP and Modbus/RTU
The device supports both Modbus/TCP and Modbus/RTU communication. Modbus/TCP uses the
Ethernet connection to communicate with Modbus/TCP clients. Modbus/RTU is a serial protocol that
can be selected for the available serial ports.
The following Modbus function types are supported:
• Read multiple holding registers (function code 3)
• Write single holding register (function code 6)
• Write multiple holding registers (function code 16)
• Read/Write multiple registers (function code 23)
The following data can be accessed using both Modbus/TCP and Modbus/RTU:
• Device measurements
• Device I/O
• Commands
• Events
• Time
Once the configuration file has been loaded, the user can access the Modbus map of the relay via the
AQtivate software (
Tools
→
Communication
→
Modbus Map). Please note that holding registers start
from 1. Some masters might begin numbering holding register from 0 instead of 1; this will cause an
offset of 1 between the relay and the master. Modbus map can be edited with Modbus Configurator
(
Tools
→
Communication
→
Modbus Configurator).
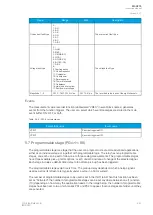
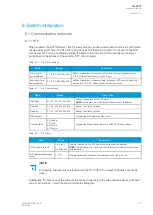
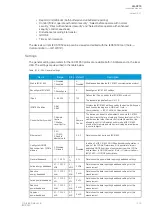
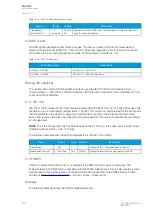
Table. 6.1.3 - 220. Modbus/TCP settings.
Parameter
Range
Description
Enable Modbus/
TCP
0: Disabled
1: Enabled
Enables and disables the Modbus/TCP on the Ethernet port.
IP port
0…65 535
Defines the IP port used by Modbus/TCP. The standard port (and the default
setting) is 502.
Ethernet port
0: All
1: COM A
2: Double Ethernet card
Defines which ethernet ports are available for Modbus connection.
Event read mode
0: Get oldest available
1: Continue previous
connection
2: New events only
0: Get oldest event possible (Default)
1: Continue with the event idx from previous connection
2: Get only new events from connection time and forward.
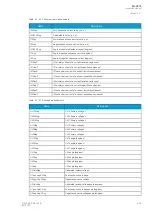
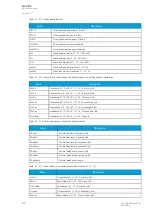
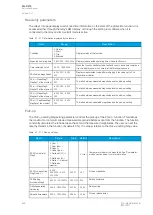
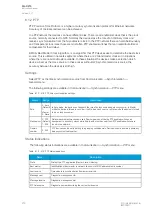
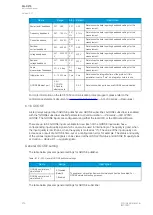
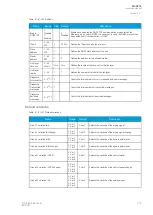
Table. 6.1.3 - 221. Modbus/RTU settings.
Parameter
Range
Description
Slave address
1…247
Defines the Modbus/RTU slave address for the unit.
A
AQ
Q-C215
-C215
Instruction manual
Version: 2.07
© Arcteq Relays Ltd
IM00040
273