Service Guide E8364-90001
4- 23
PNA Series Microwave Network Analyzers
Troubleshooting
E8362A, E8363A, E8364A
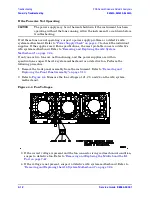
Rear Panel Troubleshooting
LAN Troubleshooting
Problems with the Local Area Network (LAN) can be difficult to solve. Software and
protocol problems can make it difficult to determine whether the analyzer’s hardware is
working properly, or if there is a problem with the LAN or cabling.
The purpose of this section is to determine if the analyzer’s hardware is functioning
properly. While the turn-on self-test verifies some LAN hardware functionality, it is limited
to internal testing only. Incorrect IP addresses will prevent proper operation. Improper
subnet masks may allow only one-way communication, while improper gateway addresses
may exclude outside LAN access.
Ping Command
The analyzer has the built-in capability of performing a “ping” operation. Ping will request
the analyzer to send a few bytes of information to a specific LAN device. That device will
then signal the analyzer that it has received the information. The analyzer computes the
approximate round trip time of the communication cycle and displays it. For a full test of
two-way communications, a ping test should be performed in two directions.
•
First
: you should ping from the analyzer to the local area network.
•
Second
: you should ping from the local area network to the analyzer.
NOTE
In the second case, any other network device capable of sending a ping
command could be used, assuming it is connected to the same network. This
could be a computer or even another analyzer.
How to Ping from the Analyzer to the Local Area Network (LAN)
Follow the steps below to verify proper LAN operation (assuming you have a functioning
LAN). If no network LAN is available, see
“Testing Between Two Analyzers” on page 4-25
1. Make sure the IP address on the analyzer is set properly and that it is unique. If unsure
how to check the IP address, refer to the embedded help in the analyzer.
2. Make sure the subnet mask is
0.0.0.0
. If not, note the current setting (to allow setting
it back later) and then set it to
0.0.0.0
. If unsure how to check the subnet mask, refer
to the embedded help in the analyzer.
3. Find and note the IP address of another working LAN device on the same network.
Make sure this device is turned on, connected, and is functioning properly.
4. To ping the network device:
a. On the
System
menu, click
Windows Taskbar
.
b. On the
Windows Taskbar
menu, point to
Programs
,
Accessories,
and then click
Command Prompt.
c. The command prompt window is displayed.
d. At the prompt, type
ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
1
and press
Enter
on the front panel or
keyboard. Refer to Step 5 for the results of a successful ping.
1.
The letters x represent the IP address of the other device on the network.
Summary of Contents for E8362A
Page 11: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 1 1 1 Safety and Regulatory Information ...
Page 19: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 2 1 2 General Product Information ...
Page 29: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 3 1 3 Tests and Adjustments ...
Page 79: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 4 1 4 Troubleshooting ...
Page 139: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 5 1 5 Theory of Operation ...
Page 169: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 6 1 6 Replaceable Parts ...
Page 215: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 7 1 7 Repair and Replacement Procedures ...
Page 287: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 A 1 A Error Terms ...
Page 303: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 B 1 B Option Enable Utility ...
Page 309: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 C 1 C Firmware Upgrades ...
Page 313: ...Service Guide E8364 90001 D 1 D Operating System Recovery ...