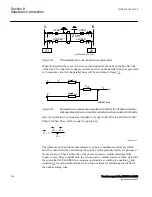
During continuous valve bypass the TCSC represents an inductive impedance of about
20% of the capacitor impedance. Both operation in capacitive boost mode and valve
bypass mode can be used for damping of power swings. The utilization of valve bypass
increases the dynamic range of the TCSC and improves the TCSC effectiveness in
power oscillation damping.
8.1.2.9
Challenges in protection of series compensated and adjacent power
lines
SEMOD168320-10 v2
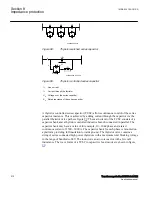
System planning does not consider any more possible protection issues and difficulties,
when deciding for a particular, non conventional solution of certain operation and
stability problems. It is supposed that modern communication and state of the art
computer technologies provides good basis for the required solution. This applies also
to protection issues in series compensated networks. Different physical phenomena,
which influence conventional principles of IED protection, like distance protection,
phase comparison protection, are well known and accordingly considered in IED
design. Some other issues, like influence of controlled thyristors in series capacitor
banks are getting increased importance, although not as high as they would deserve.
The most important challenges, which influence the operation of different protection
functions in the greatest extent, are described in this chapter.
Voltage and current inversion
SEMOD168320-168 v2
Series capacitors influence the magnitude and the direction of fault currents in series
compensated networks. They consequently influence phase angles of voltages
measured in different points of series compensated networks and this performances of
different protection functions, which have their operation based on properties of
measured voltage and current phasors.
Voltage inversion
SEMOD168320-171 v2
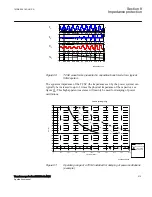
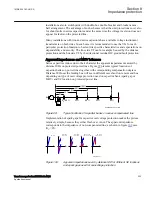
presents a part of series compensated line with reactance X
L1
between the
IED point and the fault in point F of series compensated line. The voltage measurement
is supposed to be on the bus side, so that series capacitor appears between the IED
point and fault on the protected line. Figure
presents the corresponding phasor
diagrams for the cases with bypassed and fully inserted series capacitor.
Voltage distribution on faulty lossless serial compensated line from fault point F to the
bus is linearly dependent on distance from the bus, if there is no capacitor included in
scheme (as shown in figure
). Voltage V
M
measured at the bus is equal to voltage
drop
D
V
L
on the faulty line and lags the current I
F
by 90 electrical degrees.
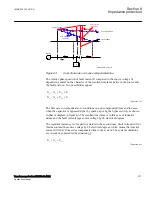
The situation changes with series capacitor included in circuit between the IED point
and the fault position. The fault current I
F
(see figure
) is increased due to the series
capacitor, generally decreases total impedance between the sources and the fault. The
Section 8
1MRK 504 163-UUS A
Impedance protection
214
Transformer protection RET670 2.2 ANSI
Application manual
Summary of Contents for RELION RET670
Page 1: ...RELION 670 SERIES Transformer protection RET670 Version 2 2 ANSI Application manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 48: ...42 ...
Page 64: ...58 ...
Page 74: ...68 ...
Page 104: ...98 ...
Page 194: ...188 ...
Page 518: ...512 ...
Page 618: ...612 ...
Page 648: ...642 ...
Page 666: ...660 ...
Page 672: ...666 ...
Page 682: ...676 ...
Page 844: ...838 ...
Page 868: ...862 ...
Page 956: ...950 ...
Page 964: ...958 ...
Page 1004: ...998 ...
Page 1014: ...1008 ...
Page 1015: ...1009 ...